& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
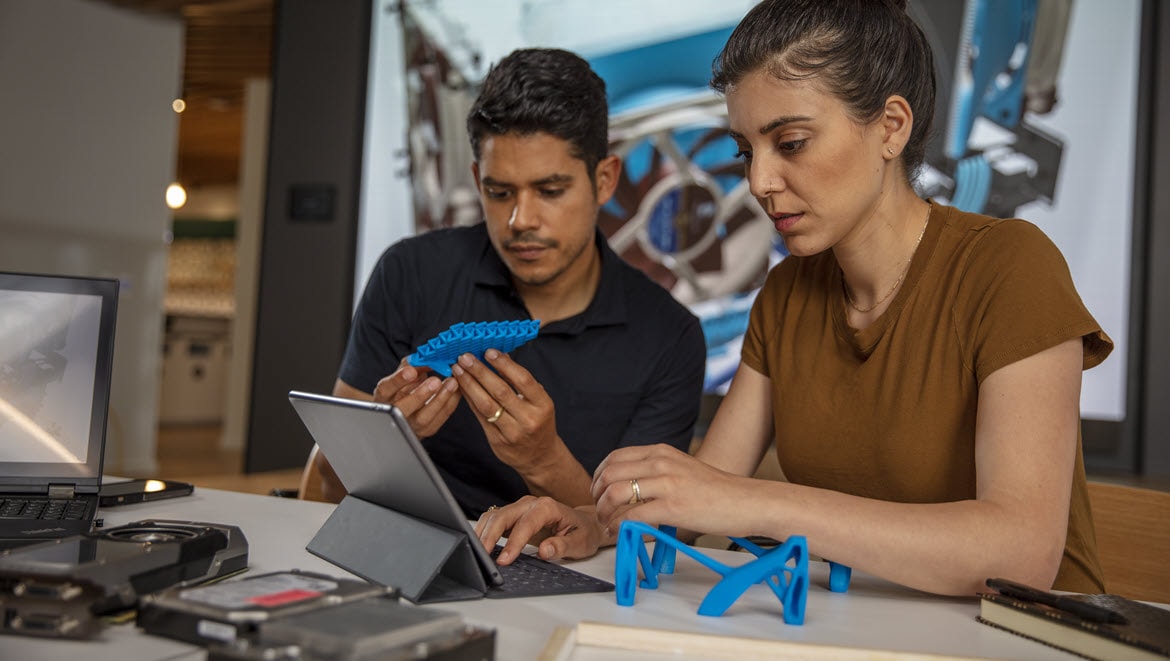
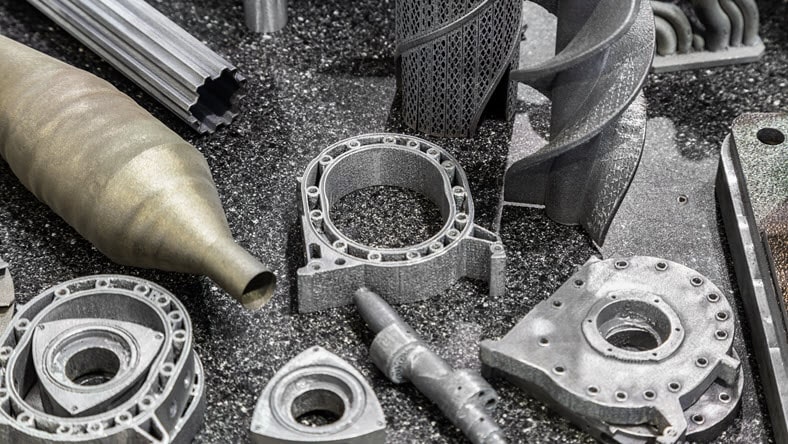
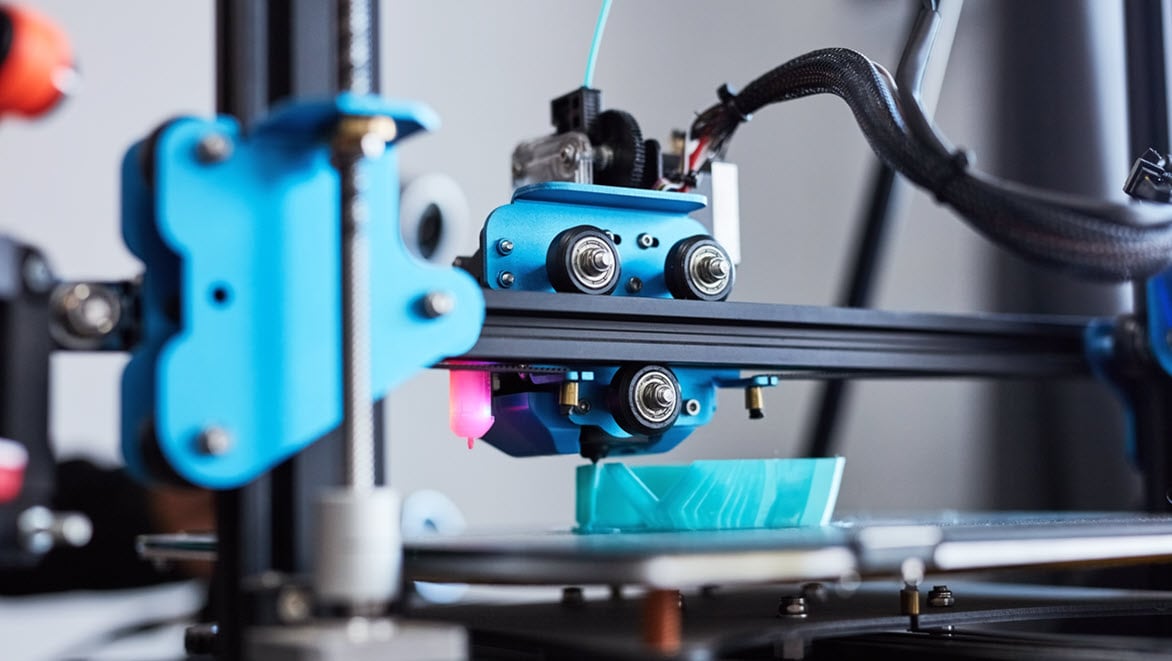
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process used to create a physical (or 3D) object by layering materials based on a digital model. Unlike subtractive manufacturing, which creates its final product by cutting away from a block of material, additive manufacturing adds material to form its final product.
Additive manufacturing expedites prototyping, allowing designers, engineers, and manufacturers to quickly refine designs, saving time and reducing costs. Additive manufacturing also enables customized manufacturing and promotes sustainability through the reduction of waste and energy consumption.
Additive manufacturing software supports and optimizes the entire process of additive manufacturing. It plays a critical role in 3D printing workflows, from design and modeling to planning, slicing, and machine control.
Additive manufacturing software allows creators to produce fully prepped design files and connect directly to 3D printing machines.
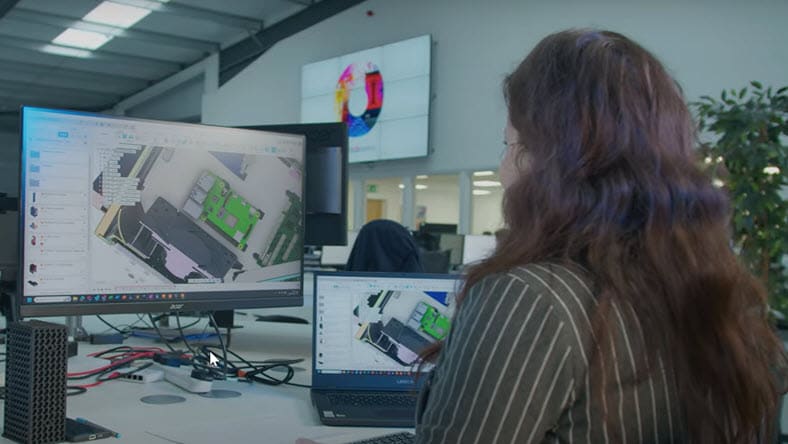
Additive manufacturing is primarily used by engineers, architects, and construction managers, and has replaced manual drafting. Manufacturing software helps users create designs in three dimensions to visualize construction and enables the development, modification, and optimization of the design process.
This process helps engineers make more accurate representations and modify them more easily to improve design quality.
Here are the key benefits of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing.
Additive manufacturing enables the creation of intricate and complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. It also allows for the production of custom parts tailored to specific needs.
Additive manufacturing allows for quick iterations and adjustments to designs to speed up the development process. It's also cost-effective, reducing the expenses associated with prototyping by eliminating the need for expensive molds or tooling.
Additive manufacturing uses only the material needed to create a part, resulting in less waste compared to subtractive manufacturing processes. It also contributes to sustainability efforts by minimizing material usage and reducing waste.
Additive manufacturing enables on-demand production, reducing the need for large amounts of inventory and storage space. It simplifies supply chains by allowing parts to be produced locally, thus reducing lead times and transportation costs.
Additive manufacturing eliminates the need for expensive molds and tooling, thus reducing upfront costs. It's also cost-effective for small batch production, making it suitable for low-volume manufacturing.
Additive manufacturing creates lightweight structures without compromising strength. It also offers advanced materials with properties like high strength, heat resistance, or biocompatibility.
CORE ESSENTIALS
Autodesk Fusion offers a comprehensive suite of tools catering to industrial designers, mechanical engineers, and manufacturing engineers. It provides capabilities for businesses to create CNC files (G-codes) for driving various manufacturing machinery and processes.
Fusion also supports diverse 3D printing technologies for producing prototypes, fixtures, spare parts, and more in various plastics. Further, the solution includes 3-axis CNC milling. This encompasses basic lathe operations for both small and large-scale production, working with materials like metal and wood.
Includes:
Try Autodesk Fusion free for 30-days
ADVANCED MANUFACTURING CAPABILITIES
Autodesk Fusion for Manufacturing offers advanced tools for businesses as they grow and invest in more complex machinery and production processes. Specifically, it supports 3D printing with both plastics and metals. This includes selective laser sintering and SLM, for the creation of new parts and hybrid manufacturing.
Fusion for Manufacturing also provides powerful tools for optimizing 3D printing processes. These tools include automatic part orientation, support structures, and material-based parameters, enhancing productivity and reducing waste.
Includes advanced manufacturing capabilities:
Create, modify, and optimize 3D models. Edit and repair 3D meshes, so that models are watertight and error-free for printing.
Slice the 3D model into thin horizontal layers for sequential building by the 3D printer. Also, determine the best path for the printer's nozzle or print head to improve quality and speed up production.
Select appropriate materials for 3D printing based on factors like strength and flexibility. Estimate the amount needed to aid in cost calculations and inventory management.
Generate support structures for overhanging parts to ensure stability during printing. Configure print settings such as layer height, print speed, and temperature.
Simulate the printing process to predict potential issues. Analyze the structural integrity of the design to make sure that the part meets specifications.
Interface directly with 3D printers to send jobs and monitor progress. Autodesk Fusion's cloud-based platform offers a collaborative design and manufacturing process.
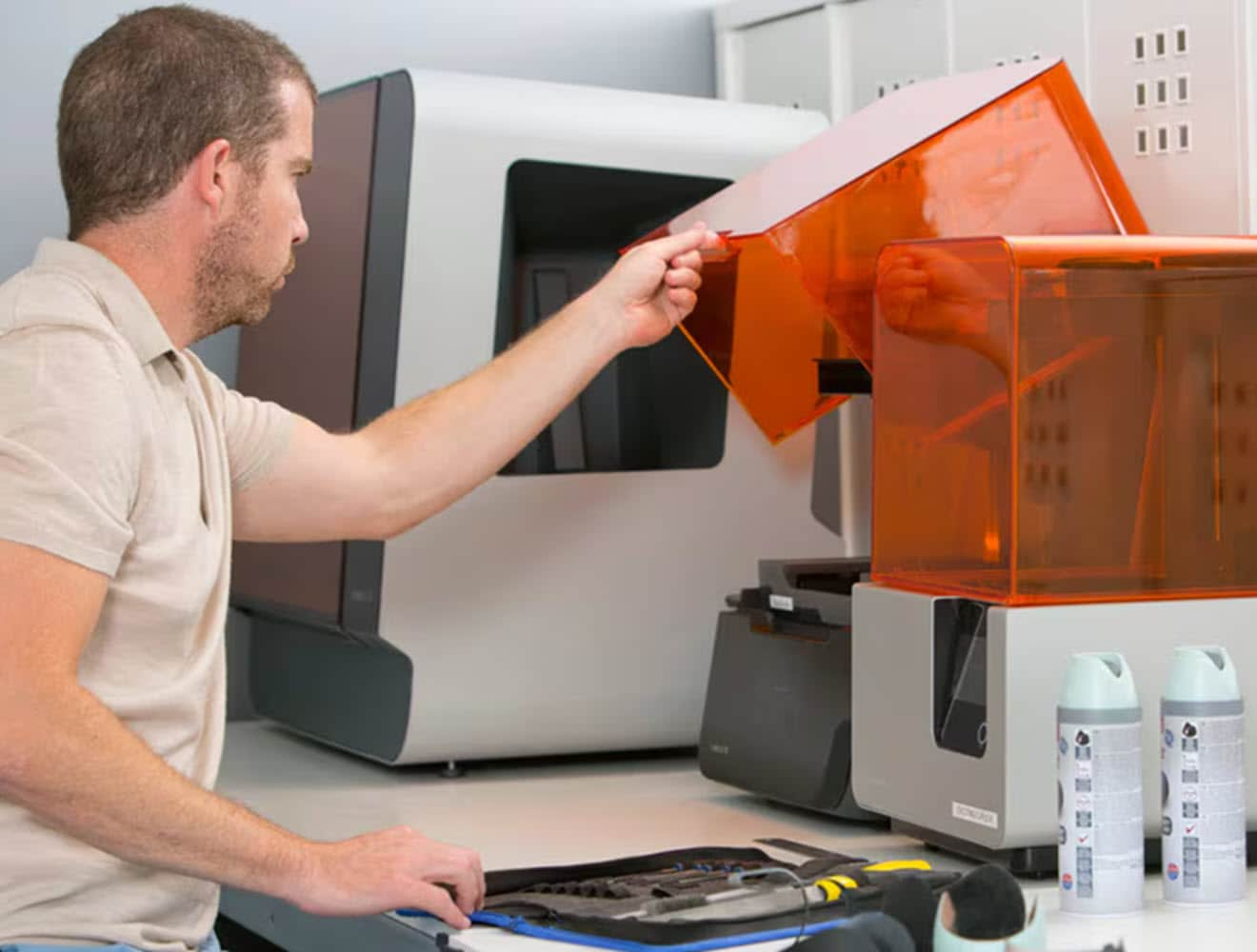
A vat of photopolymer liquid is cured by focused UV light that builds parts layer by layer for a high-detail surface finish.
A powder substrate is hardened when the printing head deposits a drop of binding fluid in a layering process. This process allows for full-color prototype fabrication.
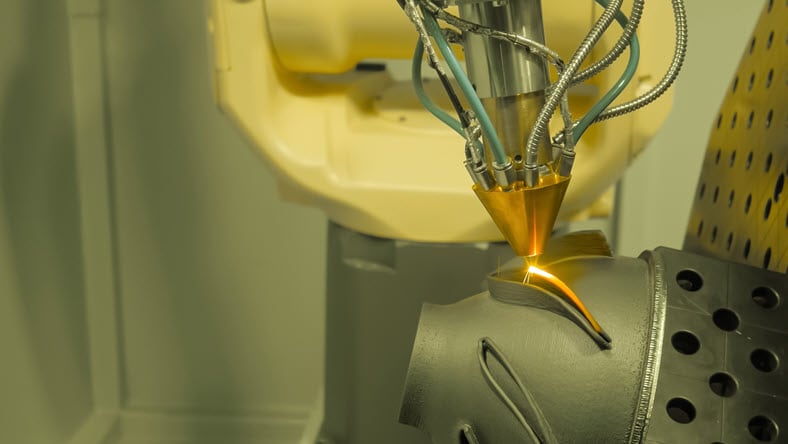
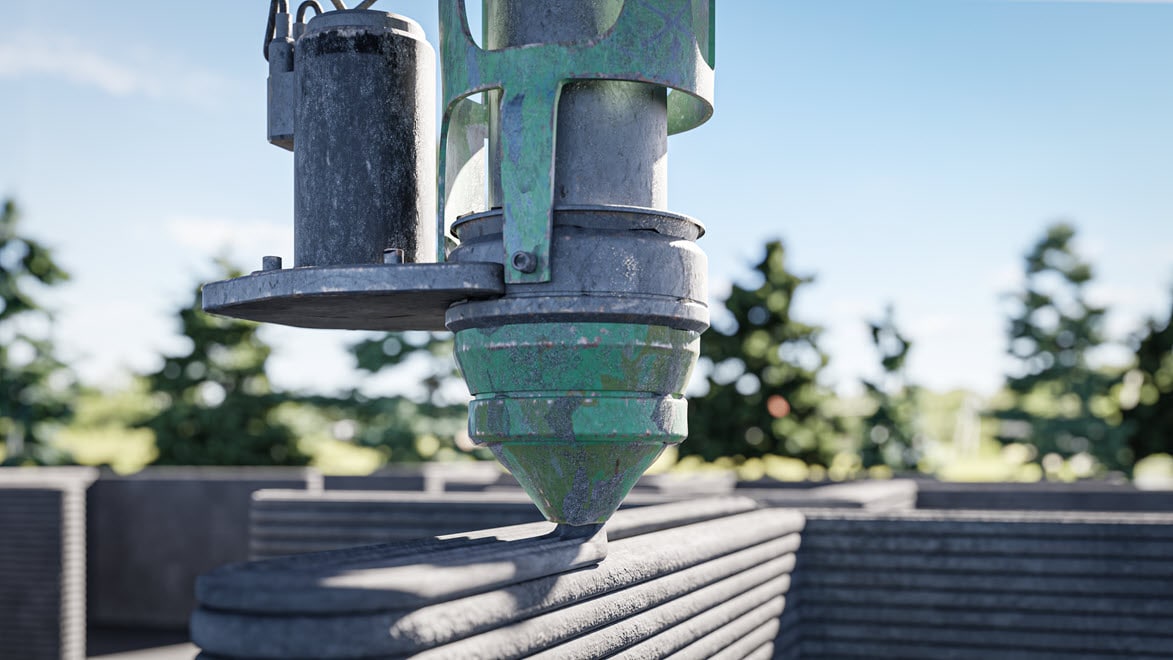
This process repairs or adds to existing components by using a multi-axis nozzle to extrude laser-melted material, commonly metal powders, onto the printing surface.
Using generative design and simulation software to produce complex metal parts helps manufacturers get more value from proven metal casting processes.
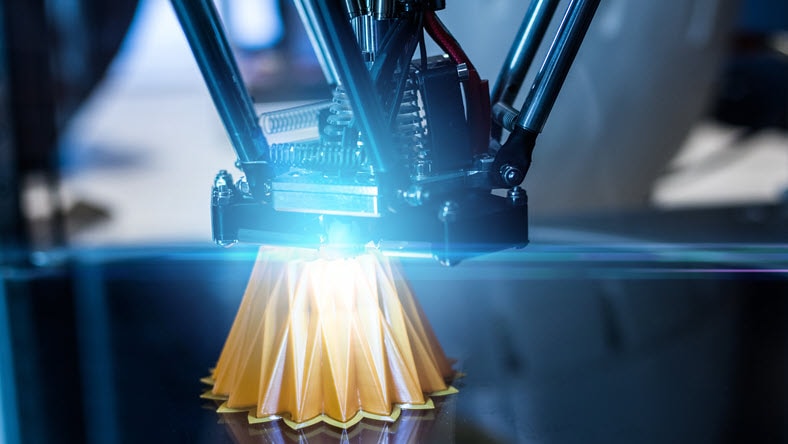
In this process, used where surface finish and form testing are needed, a printhead lays down successively solidifying layers of UV-curable material to form prototyped designs.
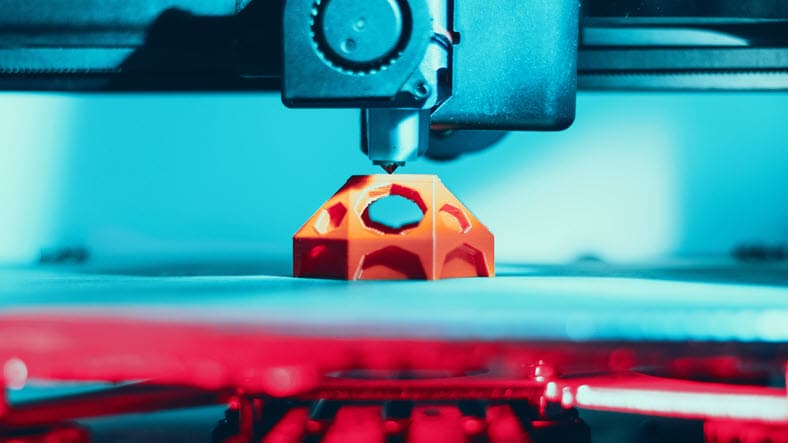
Fused deposition modeling is a common 3D printing process in which a heated nozzle extrudes a plasticized material to form products from a sliced CAD model.
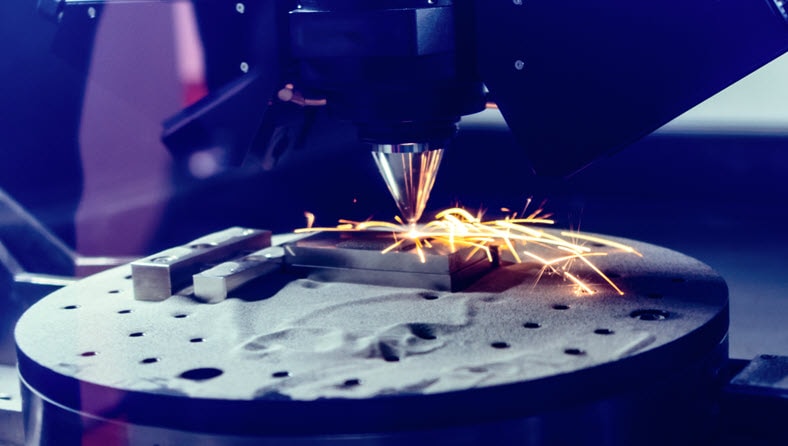
Laser or electron beams rapidly fuse layered powder material, such as various metals, together. This technique is used for circuits, structures, and parts.
Ribbons of metal or paper are bonded through ultrasonic welding or adhesive, respectively. The finished shaping is completed through further material removal processes.
Metal additive manufacturing or metal 3D printing, involves the layer-by-layer construction of metal parts using advanced technologies such as selective laser melting (SLM), electron beam melting (EBM), and directed energy deposition (DED). By precisely controlling the deposition of metal powders or wire, metal additive manufacturing can create intricate internal structures, lightweight designs, and optimized components.
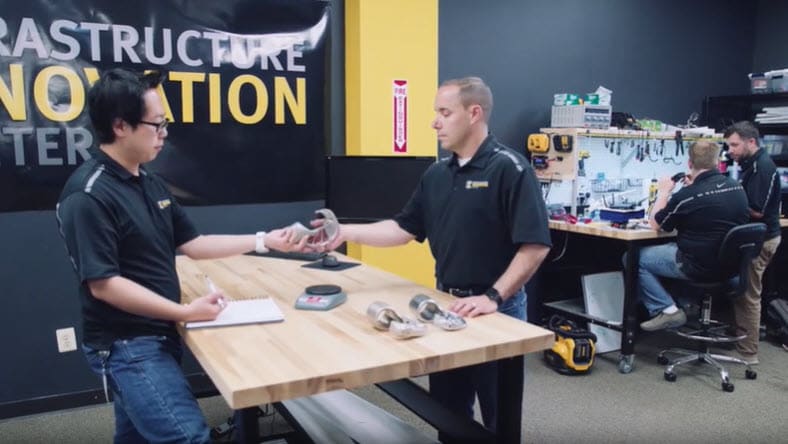
One of the key advantages of metal additive manufacturing is its capacity for rapid prototyping and reduced lead times. Engineers and designers can quickly iterate and refine their designs, accelerating the development cycle and bringing innovative products to market faster.
In 1981, Hideo Kodama of Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute published the first account of a functional rapid prototyping system using photopolymers.
Charles Hull invented stereolithography (SLA) in 1984, a method using ultraviolet lasers to harden photopolymer resin, and later founded 3D Systems Corporation, which released the first commercial SLA machine, the SLA-1, in 1988.
In 1992, Dr. Carl Deckard at the University of Texas developed the first selective laser sintering (SLS) machine.
By 1995, Stratasys, founded by Scott Crump, commercialized Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology. The term "additive manufacturing" emerged in 1997 to describe various technologies that construct objects layer by layer.
In 2005, Dr. Adrian Bowyer initiated the RepRap project to create a self-replicating 3D printer, helping to contribute to the accessibility and affordability of 3D printing.
The following year, the first commercially available Selective Laser Melting (SLM) machine was released for the production of complex metal parts.
In 2010, the MakerBot Replicator was introducted, making 3D printing accessible to a broader consumer market.
NASA tested a 3D printer in space in 2014, showcasing the potential for manufacturing in zero gravity, and in 2015, the FDA approved Spritam, the first 3D-printed drug for epilepsy treatment.
In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in 3D printing for producing personal protective equipment (PPE) and medical devices.
By 2021, researchers advanced bioprinting technologies with the goal of creating human organs and tissues for medical use. As of 2025, additive manufacturing continues to evolve, with significant advancements in materials science and printing technologies.
As technology advances, 3D printing will continue to expand, enabling the production of increasingly complex and high-performance components. Innovations in material science will introduce new, more durable, and versatile printing materials, including advanced composites, metals, and biocompatible substances.
Automation and integration with digital manufacturing processes will drive efficiency and scalability. Smart factories equipped with IoT devices and AI-driven optimization will streamline production workflows, reduce lead times, and improve quality control. Additive manufacturing will also play an important role in enabling mass customization, allowing companies to produce personalized products at scale without the traditional constraints of tooling and batch production.
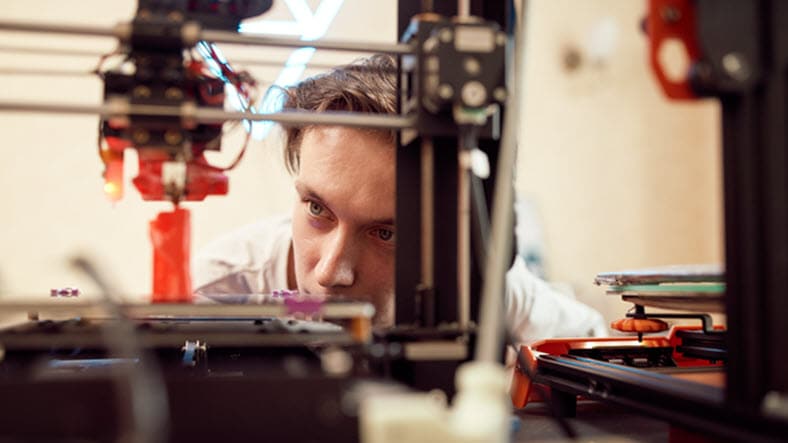
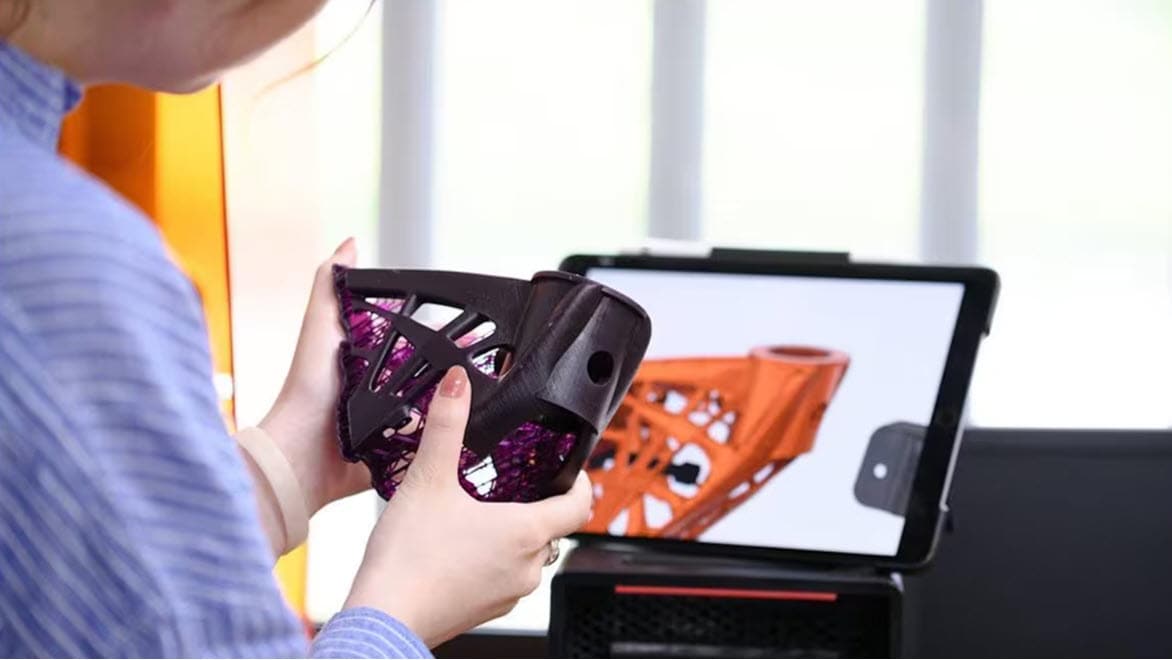
Rapid prototyping refers to the ability to quickly 3D print a new version of a product or part. It’s part of the additive manufacturing process that can be used for more effective outcomes without expensive or time-consuming prototyping stages.
Designers and engineers can use 3D printing software such as Fusion to test out many iterations of an object, and instantly print them for testing in the real world. This streamlined additive manufacturing process ensures that any potential problems are ironed out before a product launch.
Discover how our customers are using Autodesk additive manufacturing software in their projects.
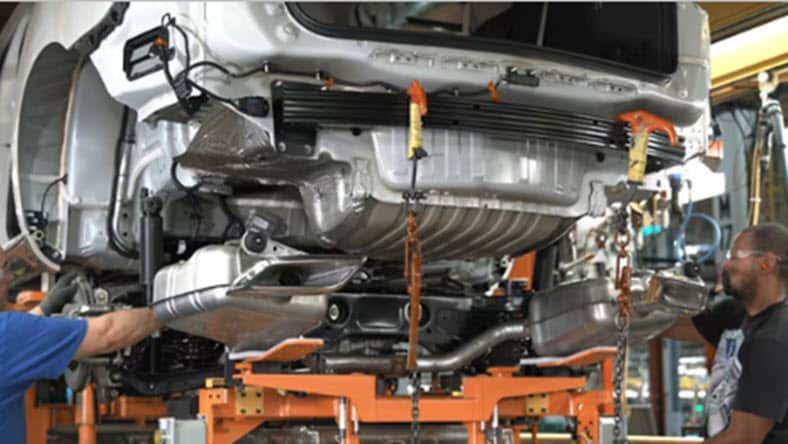
General motors
General Motors is transforming car design with additive manufacturing and generative design by creating lighter, more efficient automotive parts.
Photocentric
Learn how Photocentric uses Autodesk Fusion PCB design tools to pioneer the future of 3D printing.
Stanley Black & Decker
Black & Decker used generative design and additive manufacturing technologies to take a new approach to improve tool design.
Dr. Hannes Schwenke
Dr. Hannes Schwenke and team are 3D printing artery models to get a closer look at patient anatomy and ease patient anxiety.
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, significantly contributes to sustainability by minimizing material waste and enhancing resource efficiency. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting away excess material, additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer using only the necessary amount of material.
This process results in substantially less waste, reducing the environmental footprint of production. Additive manufacturing allows for the use of eco-friendly materials and supports localized production, which can decrease transportation emissions and energy consumption. By enabling rapid prototyping and on-demand production, it helps reduce overproduction and excess inventory, further promoting sustainable practices.
Metal additive manufacturing offers precision, efficiency, and design freedom. With advanced tools for generative design, simulation, and workflow integration, learn how Autodesk Fusion enhances the potential of metal AM.
Autodesk and SCANLAB have created a real-time closed-loop control system for laser powder bed fusion processes, enhancing precision and efficiency in additive manufacturing.
Both additive and subtractive manufacturing have revolutionized the way parts are made. Discover the difference between the two in this article.
Autodesk Fusion makes 3D printing easy by providing an integrated CAD/CAM environment, an additive manufacturing extension, helpful applications, and more.
Look at the many 3D printing applications for Autodesk Fusion to maximize your additive manufacturing capabilities.
Learn the many benefits multi-material 3D printing has in product design and manufacturing and how Autodesk Fusion can support the process.
Additive manufacturing is used to produce lighter, stronger parts and systems with greater efficiency. It has uses across various industries including:
Additive manufacturing offers several eco-friendly and sustainability benefits, including opportunities to minimize waste, optimize designs, reduce energy consumption, simplify supply chains, and enable sustainable production practices.
Additive manufacturing provides several advantages for industrial use. Significantly, additive technologies produce parts that are lighter, stronger, and faster to create than their traditional counterparts.
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is the process of adding material to create an object. Machines deposit material, layer upon layer, in precise geometric shapes, and CAD software or 3D object scanners are used to create models to direct the hardware using additive manufacturing software features.
3D printing is a more consumer-friendly phrase, and it’s becoming more and more popular in use than additive manufacturing. There are some subtle differences, however, and the term “additive manufacturing” can be used to refer to other processes such as rapid prototyping, whereas 3D printing is more restrictive.
The two phrases can best be defined as:
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer based on a digital model. This method contrasts with traditional manufacturing, which often involves subtracting material from a solid block. It allows for the production of complex geometries, customization, and material efficiency, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and the creation of intricate and personalized products. Applications span various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods, offering significant advantages in innovation and design flexibility.
The additive manufacturing process begins with creating a 3D model using CAD software, where designers can modify and optimize their designs. The model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers using software that gnerates a path for the printer's nozzle or print head. Material selection is important, as different printing technologies and applications require specific properties such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. The printing process involves layering material, whether it's plastic, metal, or another substance, to build the object incrementally. Support structures are often generated to stabilize overhanging parts during printing. After printing, post-processing steps like cleaning, curing, and surface finishing ensure the final product meets desired specifications. Simulation and analysis tools can predict potential issues and optimize the print strategy.
Additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer from the ground up using materials such as plastic, metal, or composites. This process allows for the creation of intricate and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible with traditional methods.
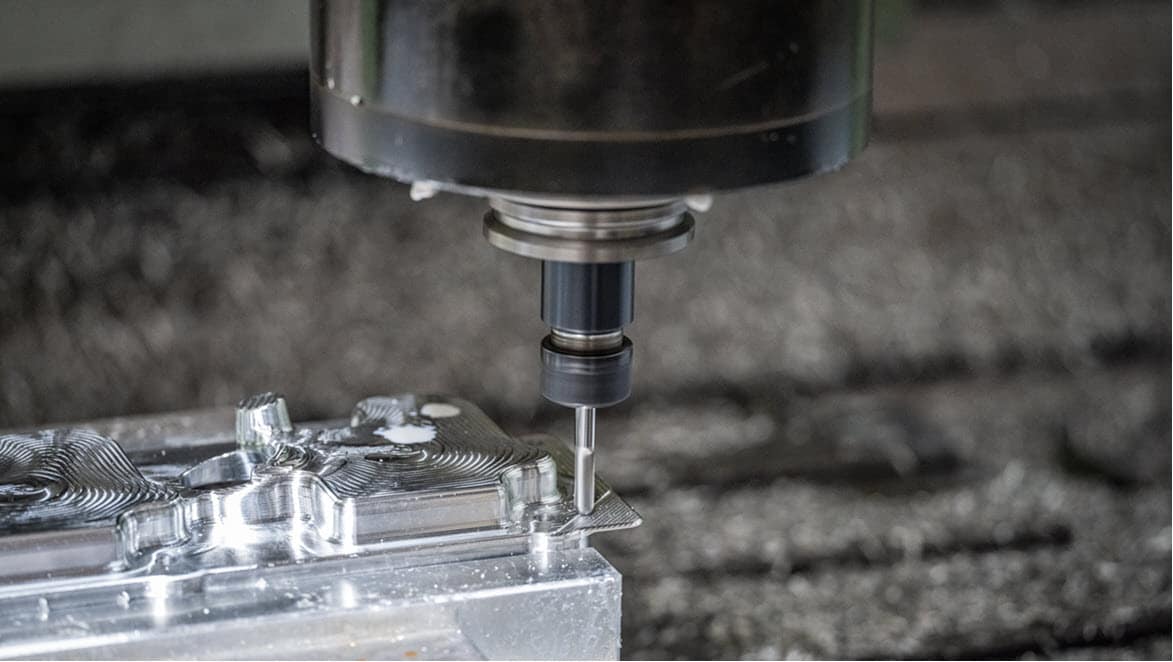
Subtractive manufacturing involves removing material from a solid block through cutting, drilling, milling, or machining to achieve the desired shape. While subtractive manufacturing is often faster for producing large quantities, additive manufacturing is more material-efficient and produces less waste.