& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
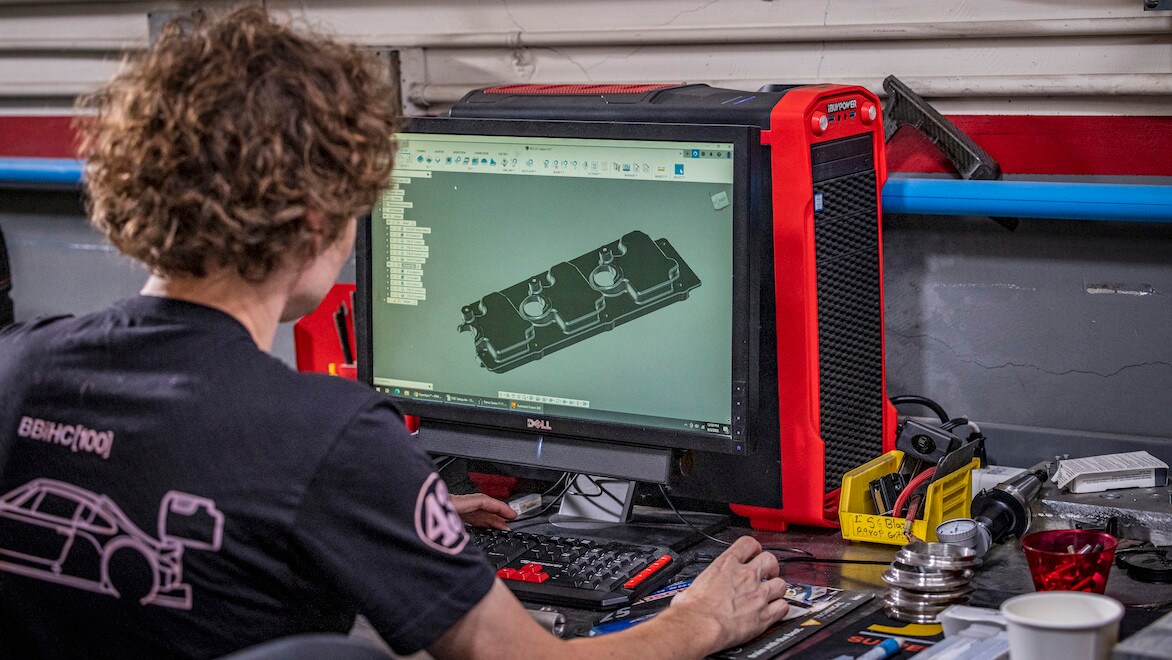
Additive manufacturing simulation software allows you to replicate real-world additive manufacturing processes. The simulation software predicts print outcomes based on the material properties and additive hardware process parameters and can be used to validate up-front engineering work or help optimize processes by visually representing design errors before they occur.
Evaluate printability, generate support structures, and optimize workspace nesting for more reliable prints.
Metal additive simulation software helps you predict print failures, improving the profitability and throughput of your additive manufacturing business.
Automatically compensate geometries based on simulation results to achieve the desired shape when your parts are manufactured or 3D printed.
Metal additive hardware and materials can be expensive. Additive manufacturing simulation software can help you minimize print failures and maximize your output, saving time, money, and frustration.
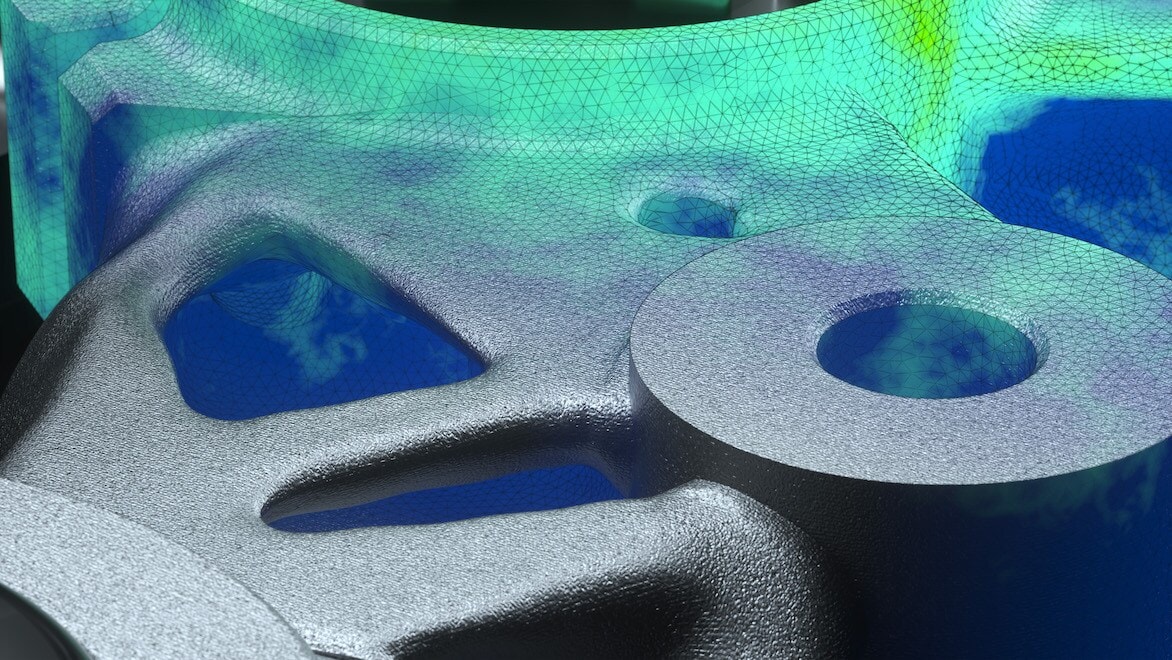
Undesirable thermal effects can lead to poor build quality. Predict regions of a build that could experience temperatures too hot or not hot enough for proper fusion during processing.
Recoater interference is a common cause of failed prints or equipment damage. Metal additive simulation software will highlight areas of potential recoater interference.
Support structures are often required to achieve a successful build with laser powder bed fusion process. Simulation software can aid in design of support structures by predicting potential failure zones.
The adaptive mesher included in Netfabb simulation uses elements only when necessary and updates the mesh with each time step to minimize compensation time for simulation solutions.
The simulation process involves mapping results from a small-scale moving source thermomechanical simulation on to a part scale thermomechanical simulation. Since this process is fully predictive and physics based, it requires no experimental calibration to achieve accurate results.
Image courtesy of MJK Performance.
The simulation software can analyze DED for both powder and wire fed systems. The DED process is simulated as a moving source thermomechanical analysis, similar to traditional weld modeling techniques. A novel element formulation and element activation approach, allows for fast simulation of each individual weld bead.
Metal parts are more commonly created through a subtractive process, which removes material. Metal additive manufacturing means to add material for the purpose of metal part creation. Metal additive materials are generally supplied as wire filaments that are heated prior to application or powders applied to the build surface by force.
Autodesk’s Netfabb and Fusion 360 Additive Build Extension simulation software let you replicate real-world metal additive manufacturing processes before going to the expense of physical manufacturing.
When it is time to produce a part, Fusion 360’s Additive Build Extension lets you configure its Manufacture workspace for the most popular metal additive 3D printers. And Fusion 360’s combination of full-featured CAD and CAM abilities allow you to craft a fully hybrid workflow that incorporates design, additive manufacturing, and subtractive surface finishing all within a single environment. Learn more about Fusion 360 Additive Build Extension.
Autodesk Netfabb supplies more extensive control on setting up and simulating your additive builds. Workflow automation, intuitive tools, and the ability to generate unique support structures and lightweight with latticing capabilities improve accuracy of your predictions on build quality and potential failure. Autodesk works with the metal additive machine manufacturers to have an extensive library of workspaces/machines to choose from. Netfabb Local Simulation includes the ability to simulate metal powder bed fusion and direct energy deposition additive processes. Learn more about Autodesk Netfabb.
Simulation software helps the metal additive manufacturing process in three ways:
Yes, Autodesk Netfabb and Autodesk Fusion 360 Additive Build Extensions work with 3D CAD native files and can be exported to 3D printable formats for easy printing.
Autodesk simulation solutions include: finite element analysis (FEA), including static stress, nonlinear static stress, quasi-static event simulation, dynamic event simulation, modal frequencies, and structural buckling; thermal (steady state and thermal stress); shape optimization (topology optimization); automated design; generative design; electronics cooling; plastic injection molding; plastic compression molding; computational fluid dynamics (CFD); and CAM toolpath simulation and engineering simualtion.
Prototyping with metal is more intensive and expensive than using more common additive materials like polymers. Every time you go back to the drawing board with your design, make an adjustment, and do a new 3D print to test performance, it compounds the delay, material waste, and cost in product testing.
Using simulation software, your part’s performance in the real world will have been comprehensively modeled and tested before you need to build a prototype, taking you from concept to production quickly and for little cost.