& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Custom manufacturing is the designing, engineering, and production of bespoke, built-to-order components and products that can’t be purchased off the shelf. Custom manufacturing software helps meet the exact specifications for one-off or small-batch products for specialized, precision industries like automotive, medical, aerospace, architecture, consumer products, and others.
Mass production methods originated during the First Industrial Revolution and have developed and matured ever since, making high-volume, highly automated manufacturing with economies of scale and low error rates possible. But traditional mass production doesn’t meet industries’ need for uniquely engineered components and products.
Many industries—automotive, aerospace, medical, architectural, energy, electronics, and consumer products, for example—need custom-manufactured one-off or small-batch parts and products. Those needs don’t often align with assembly-line mass production, where standardization is very high and implementing design changes is difficult and expensive. Custom manufacturing requires more interaction between client and producer and more human involvement with the manufacturing process than mass production to make design iterations for unlimited customization possible. Engineering a custom product is also easier using the highly reconfigurable machines used for custom manufacturing.
By its nature, custom manufacturing tends to result in higher costs and longer production times than mass production, because the upfront cost of designing, engineering, and testing a bespoke component is amortized over a smaller number of manufactured components. However, using advanced manufacturing software like Autodesk Fusion to facilitate remote collaboration on design reviews and to simulate virtual prototype testing can help narrow that gap. Fusion’s unique ability to combine both additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing (also known as hybrid manufacturing) in a single environment also has the potential to simplify the production of custom-made parts and products.
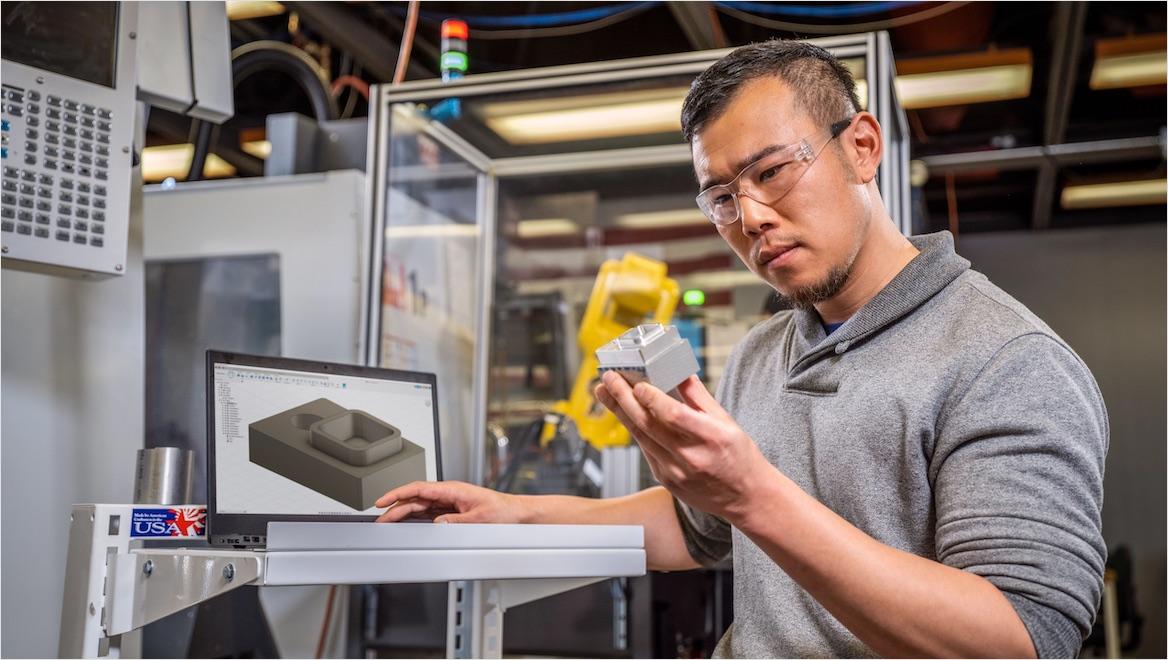
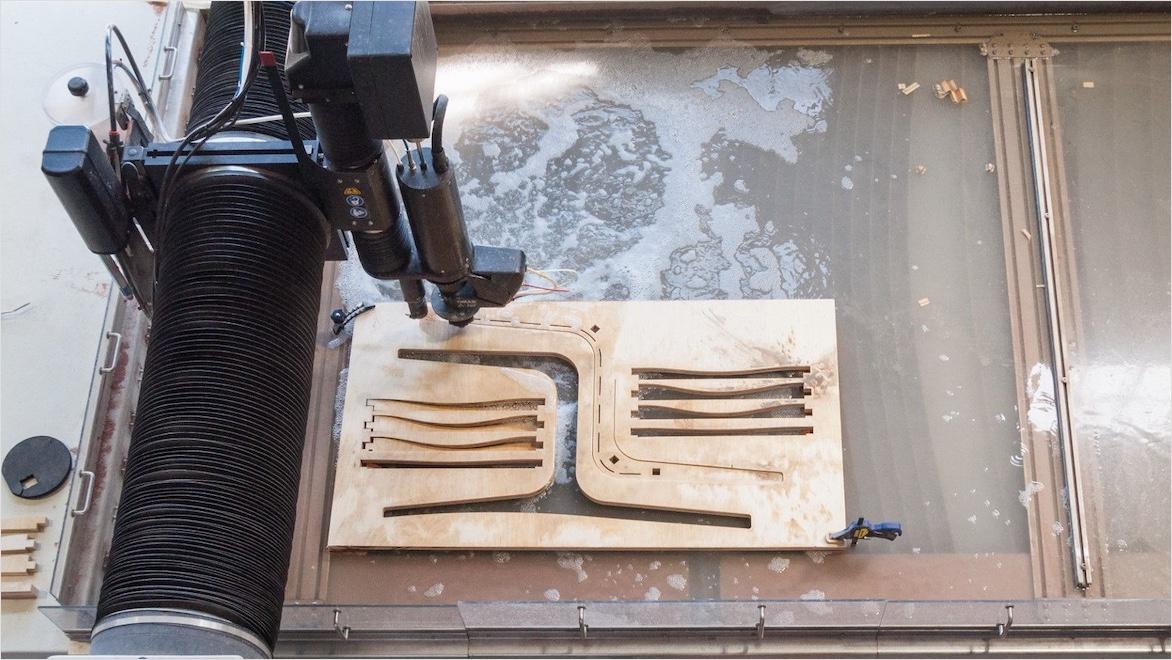
During the custom manufacturing and engineering process, the customer typically interacts to some degree with the designers, engineers, and/or fabricators doing the custom manufacturing to make sure the product meets all requirements. Before final fabrication, prototyping helps iterate the design and develop it into the desired form. Custom physical prototypes can be manufactured with the same or different methods than the final product, but common methods for making custom prototypes include additive manufacturing (3D printing), subtractive manufacturing with CNC machining or plasma/laser/water jet cutting, molding, extruding, stamping, casting, and forging.
However, physical prototyping is often time-consuming and costly, which is why many custom manufacturers have turned to virtual prototypes using prototyping software such as Autodesk Fusion. This virtual prototyping allows custom manufacturers to collaborate remotely with their clients from any computer or mobile device. Fusion’s simulation abilities can also test many aspects virtually, such as a product’s structural characteristics, electronics’ PCB layouts, and manufacturability. High-quality software rendering also enables remote, digital design reviews.
With the Fusion Xometry add-in, designers can connect to manufacturers through a large database of options and get help with manufacturability, often leading to less expensive production. All of these digital tools for prototyping can save time and costs when designing and engineering—particularly important considerations when custom manufacturing and engineering bespoke products.
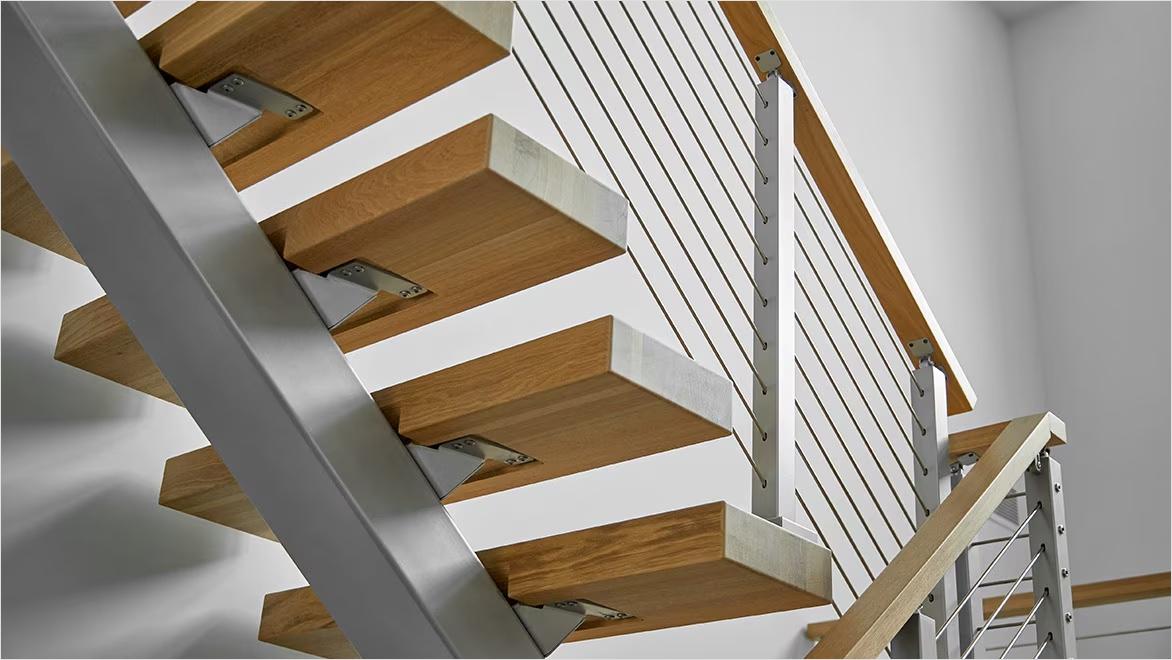
When industrialized construction can’t be used for standardized building products in the architecture, engineering, construction, and operations (AECO) industry, custom manufacturing is popular for sourcing building products that meet a project’s unique needs. Many building products are good candidates for custom manufacturing, such as lighting fixtures, enclosures, sheet goods, cabinetry, and specialized architectural and interior design elements.
Autodesk Informed Design for Inventor offers a more streamlined solution for designing customized building products. Product engineers can design building products with customizable parameters and input manufacturability information on how customization choices impact cost and lead time. Those designs then live on the Autodesk Construction Cloud database for use in BIM designs. Architects can use Informed Design for Revit to browse manufacturers’ available customizable products—such as balcony or staircase assemblies—to integrate into their building design. Certain products may have multiple release versions, and software-assisted customization is often available. This integrated approach ensures standardized and manufacturable building products, which saves everyone time: Architects don’t have to contact manufacturers to clarify their product customizations, and everyone involved in customizing these building products is guided by the documented product definition rules.
For designers and engineers, working on custom building products can be a high-pressure balancing act to meet deadlines while also focusing on product performance and profitability. Sustainability during this process may be a lower priority. However, up to 80% of a product’s lifetime emissions are determined at the design stage. Digital design software like Fusion enables engineers to weave sustainability into the design process by bringing in embodied carbon data from partners such as Makersite and MSI.
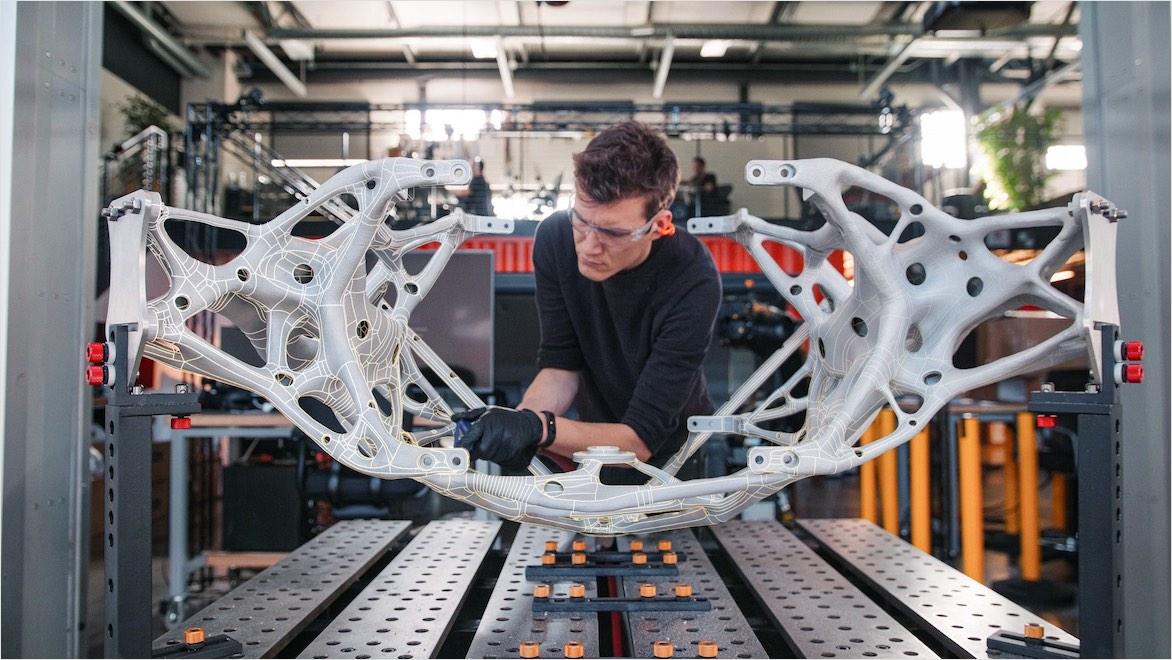
Fusion also has a robust simulation extension that allows virtual prototypes to be tested thoroughly before physical prototyping, saving substantial resources. Its generative design abilities can find solutions for components to retain strength and durability while using less material. And Fusion’s CAM capabilities can help designers choose the ideal materials and manufacturing methods for sustainability.
Using software in the custom manufacturing workflow improves and accelerates the process of communication between the client and manufacturer.
Custom manufacturing software with CAM functionality helps to optimize processes for CNC machines, 3D printers, and other machines, making costs more affordable.
Designers and engineers using custom manufacturing software can ensure that their customers receive unique products made to their exact specifications, including dimensions, performance, styling, and other design attributes.
With custom manufacturing, clients and engineers interact closely to ensure that the product requirements are met. With cloud-connected custom manufacturing software, this interaction can happen remotely in real time. Software like Fusion that combines CAM with CAD and CAE also bundles simulation, validation, and other features that help meet requirements for usability, functionality, reliability, quality, and safety.
Get Inventor + AutoCAD + Autodesk Fusion + more—Professional-grade tools for product development and manufacturing planning.
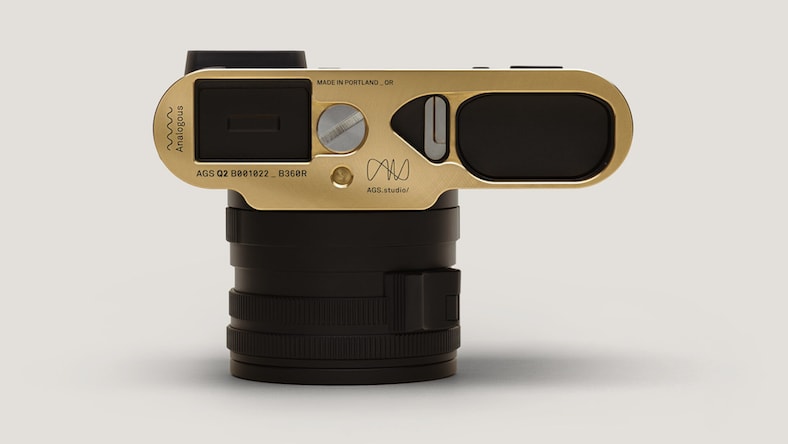
ANALOGOUS
Discover how this small Portland, Oregon CNC and custom goods shop designed and manufactured a custom baseplate for the Leica Q2 Monochrom camera, taking it from prototype to limited production run with Autodesk Fusion software.
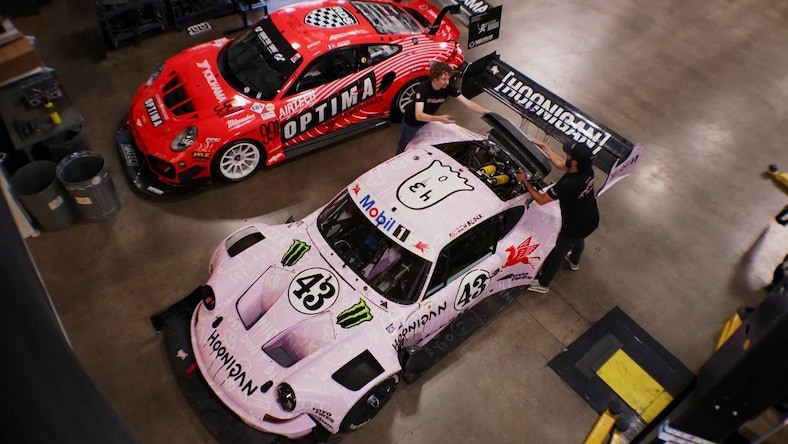
BBI AUTOSPORT
See how the automotive custom manufacturing shop from Huntington Beach, California, BBI Autosport, “built a car in Fusion,” one bespoke component at a time, with the express purpose of driving the grueling Pikes Peak International Hill Climb.
EARTHCAM
No stranger to creating custom live-streaming camera solutions, EarthCam discovered a fascinating fix for installing a high-res, low-light webcam atop the Washington Monument to broadcast a view of the National Mall, using Fusion software to design, prototype, and fabricate 18 unique parts for the enclosure.
Step inside the world of custom manufacturing service SendItCNC’s cloud-based workflow, which centers around Autodesk Fusion software to help streamline CNC CAM processes and make them more reliable and predictable.
If you’re designing custom parts but outsourcing the manufacturing, try the Xometry add-in for Fusion software. It provides instant feedback on manufacturability, as well as instant lead time and pricing info, and custom-part ordering.
Learn all about customizing machining attributes, tooling, performing custom tasks with add-ins, and more using Autodesk FeatureCAM 2024.
Watch this Autodesk University session that shows how to synchronize Autodesk Construction Cloud and Vault software to manage custom building products and projects with a single source of truth.
Custom manufacturing job shops can digitize many aspects of their operations, such as inventory management, production tracking, and scheduling, with Fusion Operations software (formerly Prodsmart). Learn how in this Autodesk University video seminar.
Britten Inc., a production house specializing in custom-built solutions, lays out the advantages of Fusion software’s generative design for creating unique parts that meet business objectives for cost, manufacturability, marketability, and more.
Custom manufacturing is on the opposite end of the production spectrum from assembly-line mass production. In custom manufacturing, a supplier designs, engineers, and produces built-to-order, one-off, or small-batch prototypes, components, and products made to the customer’s specifications.
Unlike highly automated mass production, custom manufacturing often occurs on small-shop CNC machines and 3D printers, making production highly flexible and quickly reconfigurable. Custom-manufactured goods often cost more than mass-produced counterparts and take longer to finish, but with close collaboration between the client and the engineers, custom manufacturing can deliver exactly what the customer wants.
A common example of custom manufacturing is a CNC job shop making small batches of custom components for automotive or aerospace products, or architectural building products made to fit particular structures. These include building products such as cabinetry, railings, windows, siding, and many others.
A more specialized example is a set of custom earbuds made from a digital scan to fit exactly each customer’s ear canal. A part 3D printed from the digital scan works as a mold for biocompatible silicone filling, which is then coated for the final version.
The main advantage of custom manufacturing is providing the exact solution for a customer’s needs. Whether it’s custom components for a larger assembly, custom building products, or other use cases, designers and customers can work together within cloud-based, collaborative software such as Autodesk Fusion to develop a more precise, made-to-order product that meets all requirements for dimensions, performance, quality, safety, and so on.
Fusion is also an integrated CAD/CAM/CAE solution that can optimize materials selection and custom manufacturing methods like CNC machining and 3D printing, to bring costs down closer to traditional mass-production methods.
The differences between custom manufacturing and mass production are in production quantities and methods, customer choice, and costs.
Mass production uses automated assembly lines to produce large quantities of standardized products, achieving lower costs through economies of scale. Custom manufacturing, by contrast, produces unique items that are made to order to meet the customer’s specific needs. Custom manufacturing may be automated with CNC machines, 3D printers, and more, but it produces much smaller quantities with more human involvement and usually costs more per item.
Custom manufacturing is also very flexible. Changes to the product design or manufacturing process can be made swiftly, whereas, in mass production, design or process changes are rare because they affect an entire assembly line.