& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Generative design is an advanced, algorithm-driven process, sometimes enabled by AI, used to explore a wide array of design possibilities that meet predefined criteria set by engineers or designers.
Generative design is transforming many industries by enabling optimized, efficient, and innovative solutions. In manufacturing, it facilitates the design of complex and resource-efficient parts, while in architecture and construction, it promotes sustainable, space-optimized designs. The automotive and aerospace industries benefit from significant reductions in weight and improvements in performance, and health care has advanced through customized medical devices and prosthetics. In media and entertainment, generative design helps artists bring characters, scenes, and worlds to life. Consumer goods and electronics also see innovation and efficiency gains, demonstrating generative design’s broad applicability.
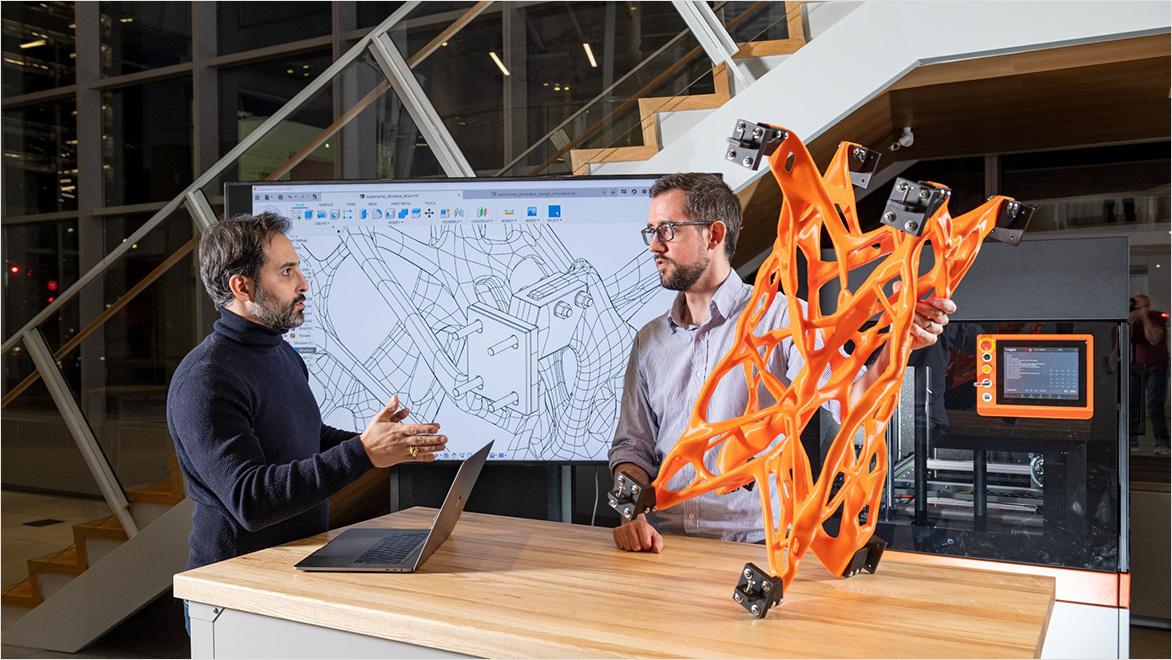
Differing from topology optimization, generative design accelerates and enriches standard engineering processes. It boosts innovation, speeds up the development cycle, and promotes sustainable material use. By automating the generation of design options, engineers can focus on optimization and customization, improving product performance without added complexity or cost. While topology optimization focuses on material distribution within a space for structural efficiency, generative design explores a wider array of possibilities, generating multiple solutions that consider functionality, manufacturability, and cost, offering a more versatile approach to design challenges.
Generative design in the architecture, engineering, construction, and operations industry enables innovative, efficient, and sustainable designs by optimizing architectural concepts, urban layouts, structural integrity, and energy usage through advanced computational methods. It streamlines construction processes and improves long-term building operations, transforming design, construction, and facility management practices with enhanced efficiency and sustainability.
Generative design is transforming the design and manufacturing industry by automating the creation of optimized, innovative product designs that meet specific performance, material, and manufacturing requirements. This approach accelerates product development, promotes sustainability through material and energy efficiency, and enables customization across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
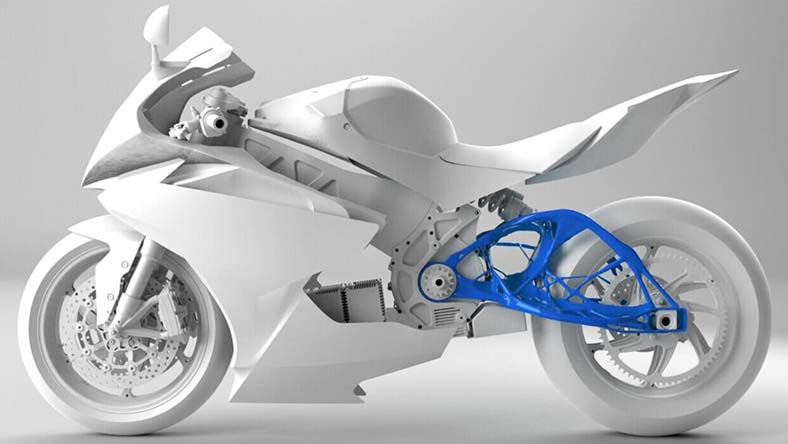
Image courtesy of Lightning Motorcycles
Generative design in the media and entertainment industry enhances content creation by enabling the automatic generation of complex visual elements, such as patterns, environments, and characters, based on predefined criteria. This approach streamlines production processes for animation, games, and virtual reality and also fosters creativity and customization, leading to more engaging and personalized user experiences.
Generative design offers transformative benefits across a range of industries by harnessing computational power to explore vast design possibilities:
Generative design pushes the boundaries of conventional design and engineering, encouraging innovation by generating novel design options that might not be immediately apparent through traditional methods.
By automating the design exploration process, generative design significantly reduces the time from concept to prototype. This acceleration enables faster iteration cycles.
Generative design optimizes materials use by suggesting structures that achieve the desired strength and functionality using the least amount of material possible.
Generative design has evolved beyond experimental stages into practical, real-world applications across many industries. Discover how leading-edge companies are using this technology today.
Innovative car manufacturers are using generative design technology to lighten the weight of vital components, merge multiple parts into one, and deliver better performance to customers.
The aerospace industry is using generative design technology to build lighter, more fuel-efficient planes while maintaining safety and performance. With generative design, innovative engineers can make flights more sustainable.
Generative design is disrupting product development in the consumer goods industry. Forward-thinking companies can create multiple options that achieve a balance of weight, comfort, durability, and performance.
Leaders in architecture and construction are using generative design to push beyond traditional boundaries. Autodesk’s Toronto office serves as a prime example; its three floors were developed based on thousands of options created with generative design.
Specialty equipment manufacturers are using generative design to create parts that use less material while maintaining structural integrity and strength. Designers are wielding the new tools to boost performance, reduce costs, and innovate faster.
Building products suppliers are using generative design and additive manufacturing to streamline complex assemblies. HVAC system manufacturers can consolidate ductwork components, reducing waste and enhancing airflow.
Edera Safety
A design studio uses generative design technology to create a rotational spine protection device for athletes.
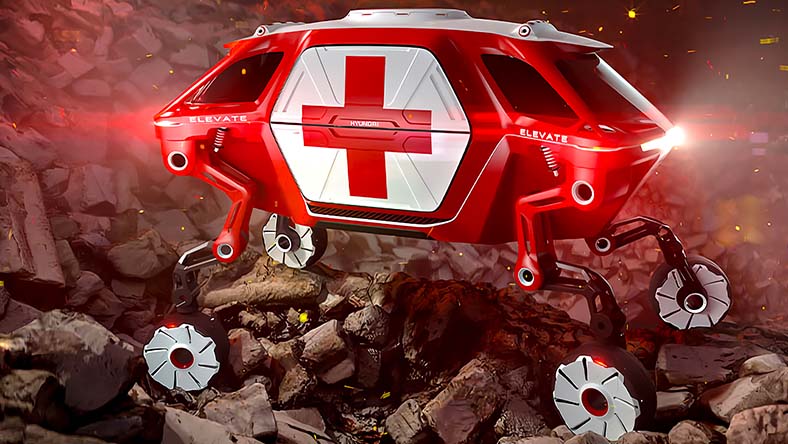
HYUNDAI
A specialized car manufacturing unit uses generative design to create a vehicle capable of going where traditional cars can’t.
Image courtesy of Hyundai
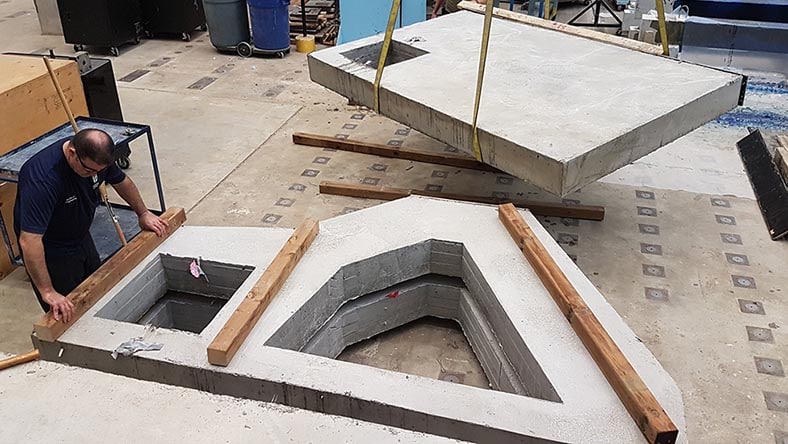
Hone Structures
A team of engineers is revolutionizing construction with generative design, AI, and robotics to enhance concrete efficiency and durability.
Image courtesy of BRAVO Engineering
AI, XR, and emerging technologies are drastically reshaping the generative design landscape, pushing the boundaries of efficiency, innovation, and collaboration. McKinsey’s projection that generative AI could deliver between $2.6 to $4.4 trillion in productivity value underscores its transformative potential.
With McKinsey’s estimate that half of today’s work activities could be automated between 2030 and 2060, the integration of AI and generative design signals a profound shift in how industries approach product development. XR technologies further amplify this impact by enhancing design visualization and interaction, making complex designs more accessible and understandable. Simultaneously, 3D printing and IoT technologies enable the realization and refinement of these designs based on actual performance data. These advancements suggest a future where generative design can streamline design processes and also redefine roles, productivity, and innovation across industries.
Grasp the core concepts of generative design across industries and see how Autodesk Research is using it in the architecture, engineering, construction, and operations industry.
Learn the basics of creating parts with generative design in product-development software.
Explore new possibilities with the combined power of generative design and generative AI.
Generative design is often powered by artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning algorithms, but it isn’t solely defined by AI. Generative design represents a broader methodology that uses computational algorithms to generate design options based on specified criteria and constraints. So, while AI can play a crucial role in enabling more advanced features of generative design, such as learning from data to improve design suggestions, generative design as a concept encompasses both AI-driven and non-AI computational methods to achieve its goals.
Generative design is a mathematical process that uses computational power to run myriad precise real-world simulations to arrive at a set of optimal design solutions for a defined problem. Generative design relies on algorithms to achieve optimal results, which means that it follows a set of instructions that dictate how it accepts input data and provides output. Generative design solutions may employ AI but not always. Generative AI is a type of AI capable of producing novel creations based on pretrained deep neural networks that produce probable, albeit unvalidated, outputs.
Generative design automates the exploration of design options by defining objectives, constraints, and a design space, then employing algorithms to generate a multitude of solutions within those parameters. It uses simulations to evaluate each design against the set objectives, iteratively refining and optimizing the options. This process allows for the rapid identification of innovative and efficient designs that might not be immediately apparent through traditional methods. Ultimately, the designer selects the most promising design(s) for prototyping and further testing. Generative design significantly enhances creativity, efficiency, and the potential for innovation in the design process.
Generative design in architecture refers to the application of computational algorithms to generate a wide array of architectural design options based on predefined criteria and constraints such as site conditions, spatial requirements, environmental factors, and material limitations. This approach allows architects to explore many design possibilities quickly and efficiently, far beyond what could be conceptualized. It optimizes for various performance metrics, including energy efficiency, structural integrity, and space utilization, identifying innovative and sustainable design solutions.
One notable example of a product developed through generative design is the Airbus A320 partition wall. Airbus used generative design techniques to reimagine the partition wall that separates the passenger cabin from the galley on its A320 aircraft. The goal was to minimize weight while maintaining structural integrity and safety standards. The resulting design, often referred to as a “bionic partition,” mimics patterns found in nature that are optimized to provide strength where needed while minimizing weight. This generative design process led to the creation of a partition that is about 45% lighter than its predecessors.
Generative design methods encompass a variety of computational approaches to create optimized designs based on set parameters and objectives. One method involves the use of AI and machine learning algorithms to automatically generate solutions that meet or exceed specific performance requirements. This process allows for the exploration of geometric forms and structures that extend beyond traditional design constraints, potentially leading to highly innovative products. The generative design process does not start with an existing part or geometry; instead, it begins with defining constraints and design goals, leading to a series of auto-generated designs that fit these specifications.
The drawbacks of generative design stem mainly from its reliance on advanced technology and the challenges that come with it. Firstly, it requires significant computational resources and expertise in AI and machine learning, making it less accessible to those without the necessary technological background or resources. The heavy dependence on technology can lead to issues like software bugs or compatibility problems. There’s also the concern of biases within the algorithms, which can affect the diversity and inclusivity of the design outcomes.
Generative design, while innovative, cannot replicate the comprehensive decision-making process, creativity, and intuition of human designers. It operates within the confines of defined parameters and lacks the ability to interpret subjective elements like aesthetics, cultural significance, or emotional impact, which are crucial in design. Additionally, generative design may propose solutions that are impractical for current manufacturing capabilities, necessitating human intervention to reconcile idealized designs with real-world feasibility. The technology also faces challenges with accessibility due to its requirements of significant computational power and expertise in AI and machine learning.
Generative design is emerging as a transformative force across industries, including design and manufacturing; architecture, engineering, construction & operations; and media & entertainment, by leveraging AI and digital simulations to explore a wide array of optimized solutions swiftly. This technology significantly enhances customization, accelerates product development, promotes sustainability through material optimization, and enables the creation of complex, innovative designs that traditional methods may not conceive. Particularly in the M&E industry, generative design can revolutionize content creation by automating the generation of intricate visual elements, facilitating immersive and engaging digital experiences.