& Construction

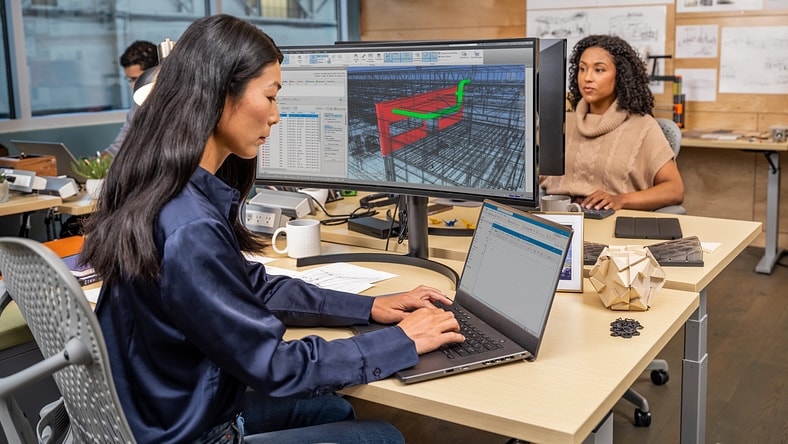
Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
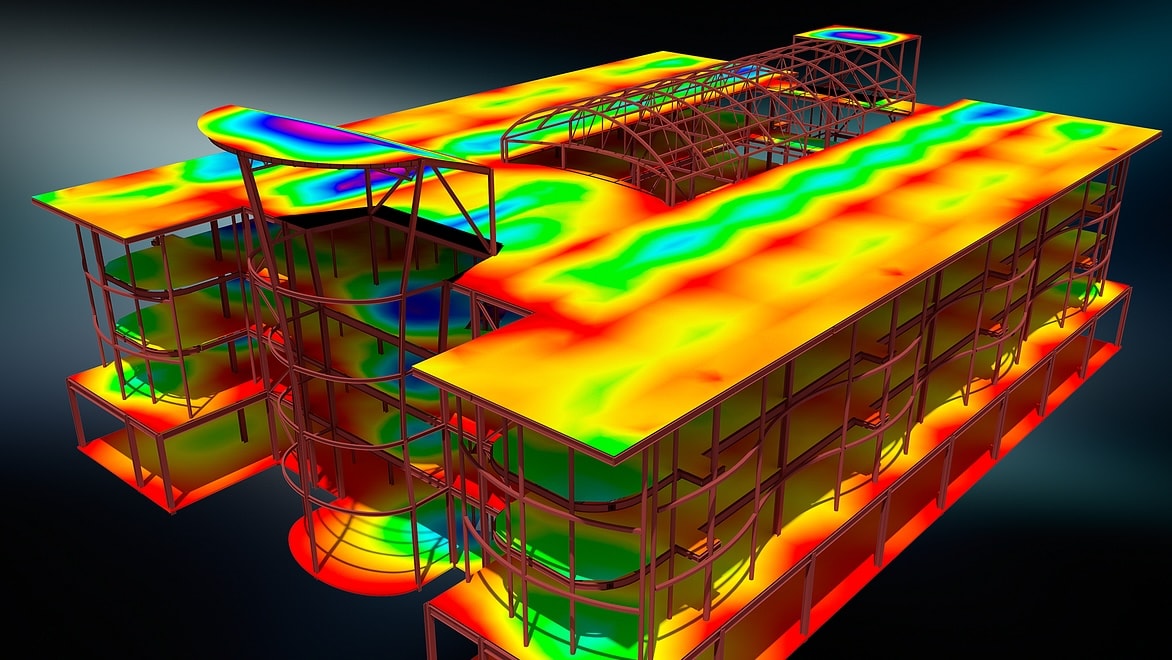
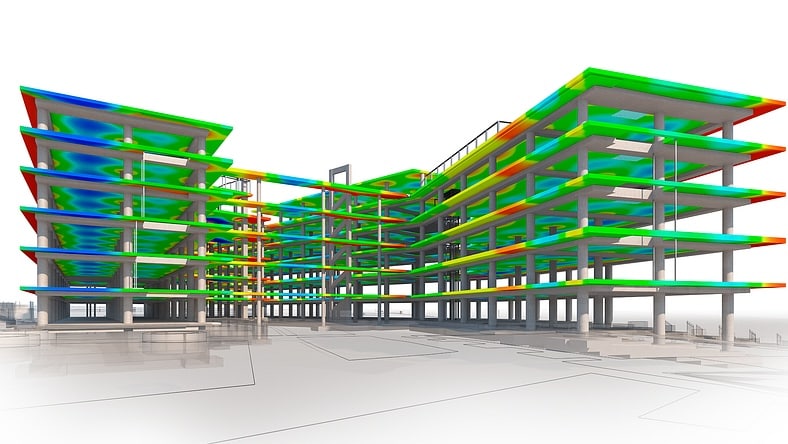
Structural analysis is a discipline within structural engineering that makes it possible to predict how structures will behave under a variety of conditions, such as when weight is applied or when environmental forces occur.
Two key components are fundamental to structural analysis: structures and loads.
Within the field of structural analysis, a structure refers to any constructed object that is built from different interconnected parts. These individual parts that make up the whole—such as beams, columns, and trusses—are known as “members.” Each of these members is designed to resist specific forces. Examples of structures include houses, skyscrapers, bridges, towers, and aircraft frames.
A load is any force that acts on these individual elements and the structure as a whole that can cause them to bend, deform, or change velocity. Structural analysis is the study and analysis of how specific loads will act upon a structure. Autodesk has a range of software that can be used in both the analysis and design of a building.
Examples of structural analysis software use can be found in many industries, including:
Structural engineers use structural analysis software to simulate the effects of various loads on proposed structural designs and materials.
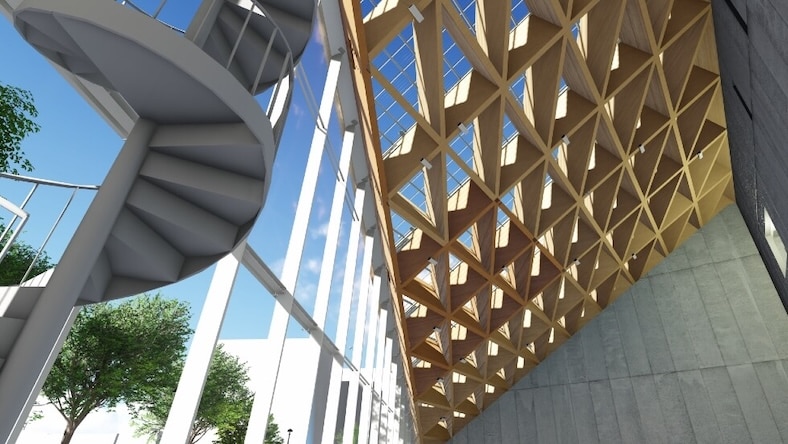
Image courtesy of BNIM
Building engineers rely on structural analysis software to assess the effectiveness of different materials and design choices.
Civil engineers employ structural analysis software to ensure that the structures they design are safe and conform to safety standards and requirements.
Before a single brick is laid, the construction team must assess the structural integrity of the structure in all possible conditions.
Architects depend on structural engineers and structural analysis programs to determine whether their designs are structurally feasible and safe.
Higher education institutions use structural analysis and design software to teach and prepare the next generation of engineers. Find out more about Autodesk’s free-to-use education licenses.
Plan, design, construct, and manage buildings with powerful tools for Building Information Modeling.
Using structural analysis software such as Robot Structural Analysis Professional or structural analytical modeling in Revit offers a number of impactful benefits, including:
In the past, engineers and designers had to complete all necessary calculations and equations manually—tasks that structural analysis programs can solve instantly and simultaneously.
Using 3D structural analysis software with advanced algorithms dramatically reduces the risk of human errors that could cause issues further down the line.
Complex structural simulations make it possible to detect flaws and weaknesses early in the design process, saving time and enhancing project safety.
Greater efficiency and accuracy mean engineers can quickly and confidently work on structural designs with high levels of complexity.
There are different types of structural analysis that can be carried out, utilizing different mathematical models, including:
Hand calculations are the oldest and most basic of analysis methods, but are still used widely to perform quick estimates and to verify the results of other analysis methods. In this method, you perform calculations on the structure and loads without the use of any software or other technology.
In finite element analysis, a structural analysis program is used to break the structure down into smaller elements, then analyze these elements to predict how the whole will behave under various forces. FEA makes it possible to run a detailed structural simulation before committing to a design in the real world.
Linear analysis is a subtype of FEA in which the relationship between forces applied to a structure and the deformations that occur is consistently in a straight line.
Non-linear analysis is used when the relationship between force and deformation is not consistent or proportional, such as when the properties of a material change when forces reach a certain point.
Tokyu Construction Co.
Tokyu Construction used structural analysis and BIM to create an efficient and reliable design.
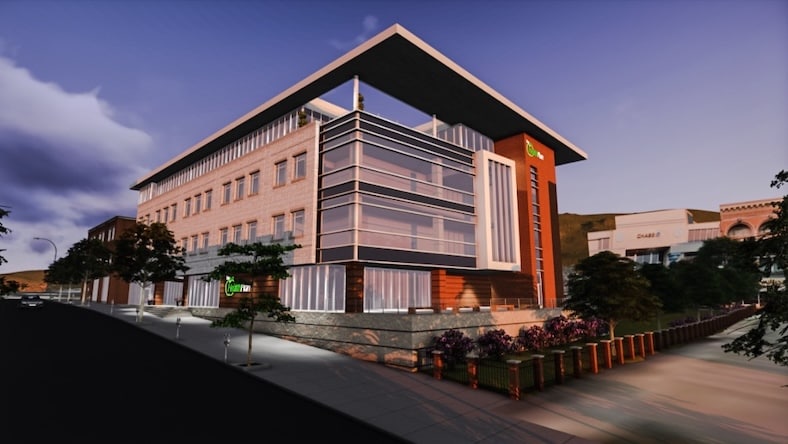
Image courtesy of Tokyu Construction Co.
Mills Group
West Virginia–based Mills group used Autodesk software for designing sustainable buildings that needed to be both efficient and structurally sound.
Image courtesy of Mills Group
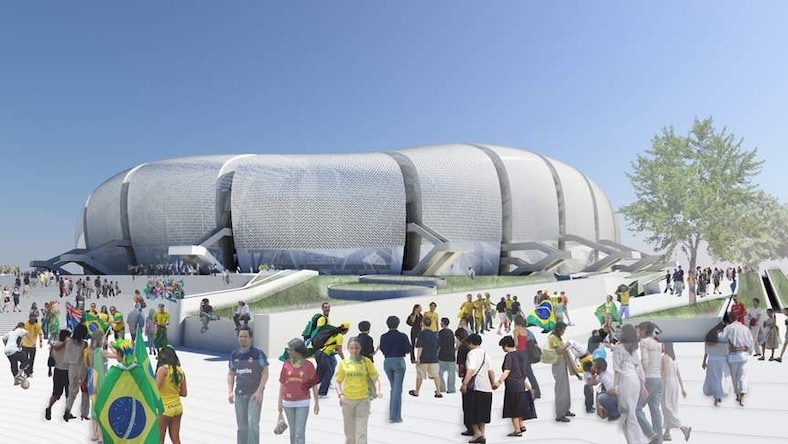
Buro Happold
Consulting engineering firm Buro Happold used Robot Structural Analysis Professional to create the Arena das Dunas stadium in Natal, Brazil.
Image courtesy of Buro Happold
GRAEF
Engineers at GRAEF used integrated BIM workflows in interoperable Autodesk software tools to bring the process of project detailing for fabrication in-house.
Image courtesy of GRAEF
Centralize decision making in Revit BIM software through integrated workflows.
Create a mesh of finite elements in minutes.
Take advantage of a virtual wind tunnel to simulate structural behavior.
Discover how to create and analyze models for concrete buildings and test designs.
See how structural analytical modeling helps engineers coordinate between physical and analytical models and workflows within Revit.
Explore the basics of using Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis Professional in a series of short videos.
Get to grips with Robot Structural Analysis Professional in our intuitive guide, featuring basic workflows incorporating modeling, analysis, design, and documentation.
Learn to model and analyze different types of structures with these simple tutorials, including 2D and 3D frame design and building design.
Take the first steps to using Robot Structural Analysis Professional from Autodesk.
While AutoCAD is not strictly designed to perform structural analysis, you can use it to create and design structures, which can then be imported into Autodesk’s dedicated structural analysis software such as Robot Structural Analysis Professional. This software is fully compatible with AutoCAD, which lacks features for making structural calculations. By designing structures in AutoCAD and then carrying out the analysis in Robot, you can achieve a seamless workflow.
Structural analysis refers to the broad practice of studying and analyzing how structures respond to forces upon them. This is done using a variety of methods. Finite element analysis, or FEA, is a specific computational method within structural analysis, which works by dividing an object into small finite elements that can be analyzed individually to determine the behavior of the whole.
To perform structural analysis, you need to first create an accurate model of your structure, then perform different calculations using methods such as thrust line analysis, limit state analysis, and finite element method. These calculations are made simple and time-efficient using Autodesk software such as Robot Structural Analysis Professional or Revit. Information needed to perform structural analysis calculations includes the geometry of the structure, structural loads, material properties, and support conditions.
The basic principles of structural analysis are: