& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
The journey from ideas to finished product is rarely a straight line, but rather a winding road filled with adjustments, improvements, and sometimes, complete overhauls. Iterative design is the backbone of this journey.
For teams and professionals in industries across Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC), Design and Manufacturing (D&M), and Media and Entertainment (M&E), the iterative design process is one through which creative ideas are transformed into real-life solutions through repeated testing, analysing, and refinement.
Iterative design is the cyclical process of rapid prototyping, testing, and refining. In this approach, designers understand that the perfect product is only achieved through continuous improvement. Instead of aiming for a perfect outcome from the start, they take each iteration as a step up a staircase that brings them closer to a final product.
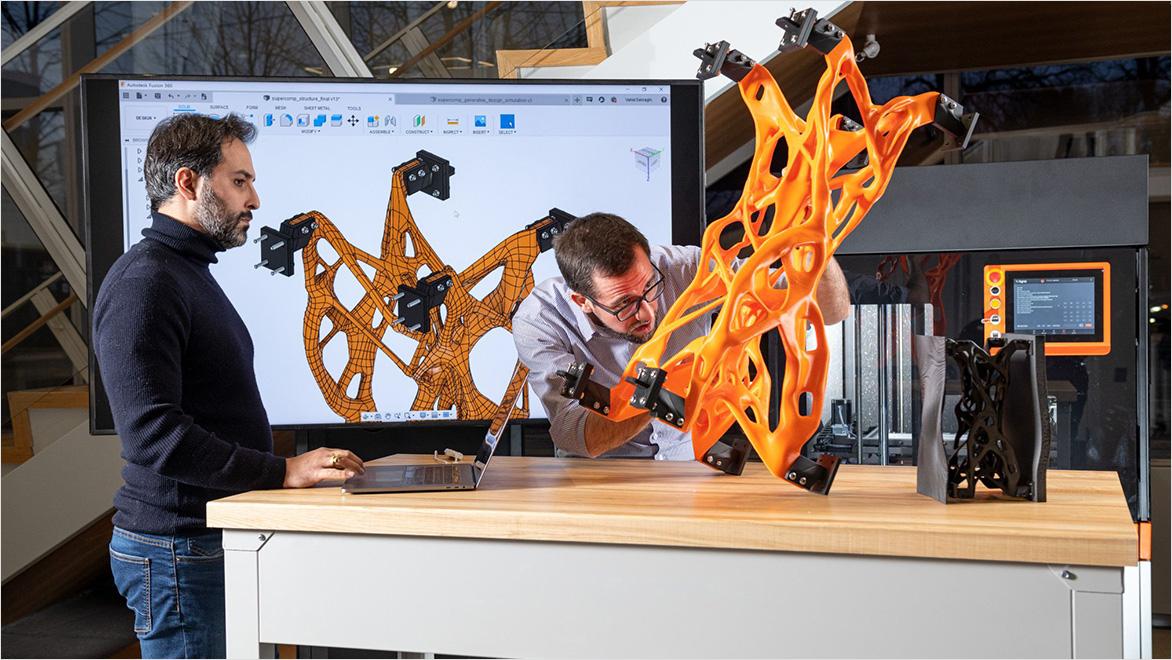
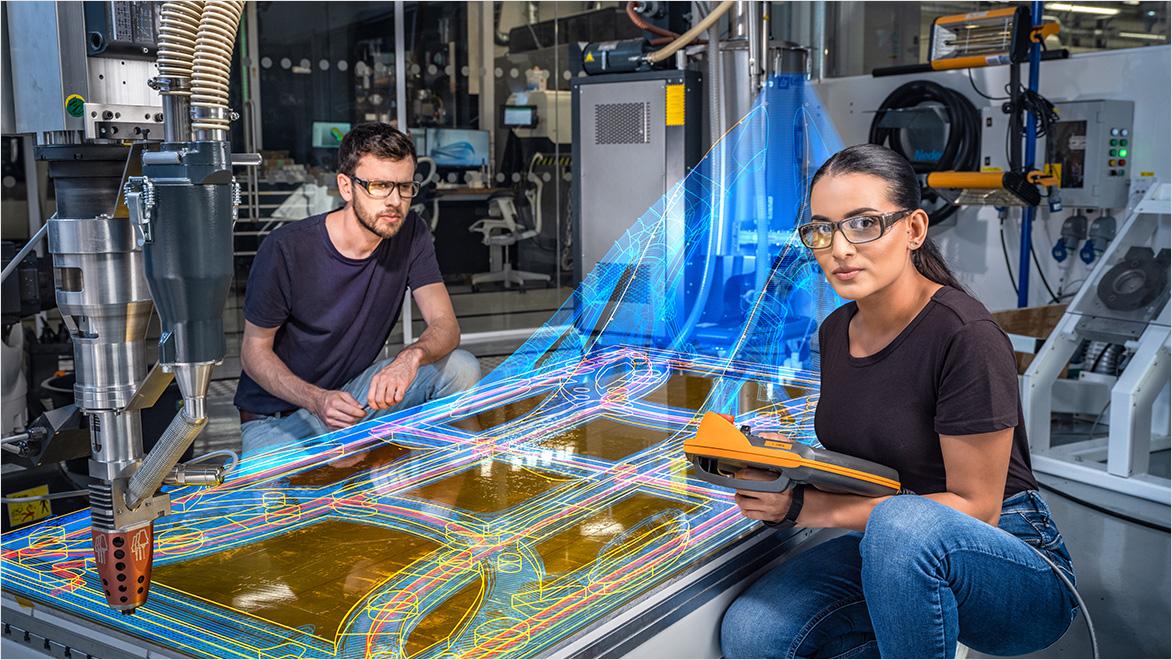
In the context of 3D modelling and smart manufacturing, the iterative design process is particularly powerful. Iterative design in 3D printing allows production designers and manufacturers to quickly create prototypes and test them in real-world scenarios. They then gather and analyse feedback from users and stakeholders. Then, they make necessary adjustments to improve the design and repeat the process all over again until they get the best results.
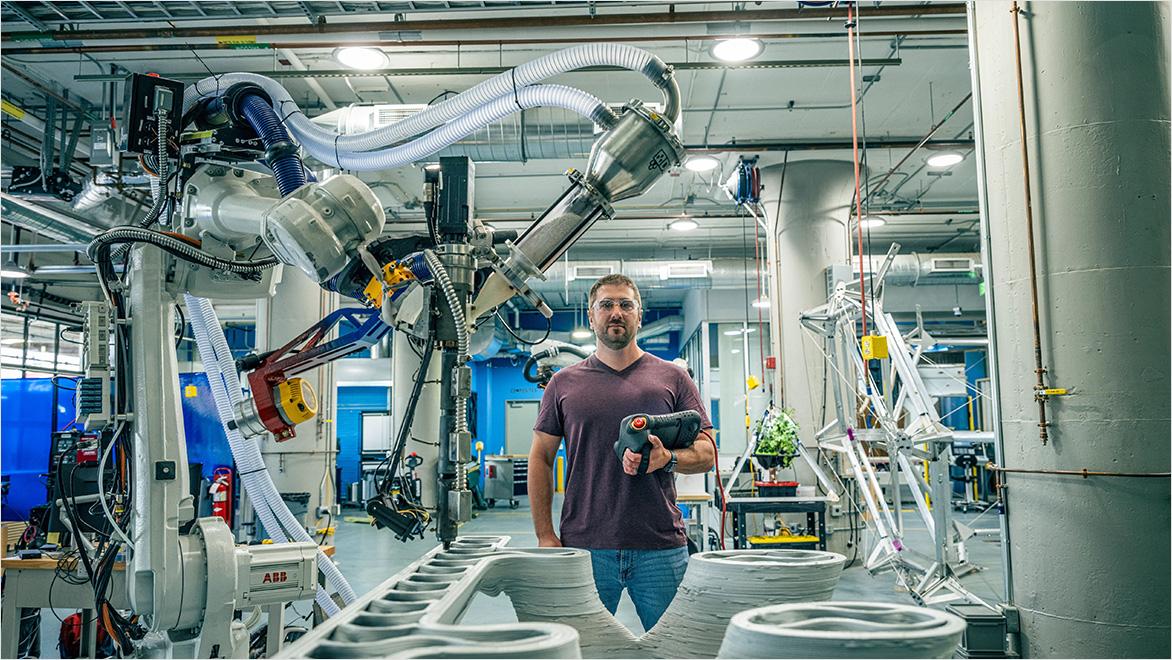
As India’s industries embrace Industry 4.0 (US Site), the integration of 3D printing and smart manufacturing is more commonplace. These technologies are naturally tied to iterative design, as they allow for rapid prototyping and quick adjustments that were previously impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. In traditional manufacturing, creating a prototype is time-consuming and expensive. Any changes to a design would require a complete overhaul of the prototype, making it daunting to take in feedback and iterate during production.
Iterative design significantly reduces this bottleneck. Production designers and manufacturers can now produce prototypes in a fraction of the time and cost, making it easier to experiment and improve ideas—with real-time monitoring and data-driven insights that lead to better iterations and products.
Let’s take a look at a few examples in the AEC, D&M, and M&E industries in India.
As India moves toward electric mobility, iterative design helps electric vehicle companies like Mahindra and Mahindra (US Site) customise key components such as battery casings and motor housings. Using manufacturing simulation software like Autodesk Fusion, EV manufacturers can evaluate prototypes through multiple iterations. India's aerospace industry also uses iterative design to develop lightweight aircraft materials, reducing fuel consumption and optimising strength-to-weight ratios.
In Bollywood, large-scale set designs are critical to creating immersive experiences. Set designers use iterative design to refine structures for stability, cost-efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. This approach is used in many Bollywood films to make props and on-set tools, as well.
Image courtesy of Hadynyah
In India’s populated urban centres, prefabricated construction is becoming essential for development. Iterative design allows construction companies to refine prefabricated modules for better energy efficiency and material usage. By leveraging 3D printing and generative design (US Site), AEC firms can produce sustainable and cost-effective housing solutions.
Plan, design, construct and manage buildings with powerful tools for Building Information Modelling.
Powerful product design and engineering tools for 3D mechanical design, simulation, visualisation and documentation.
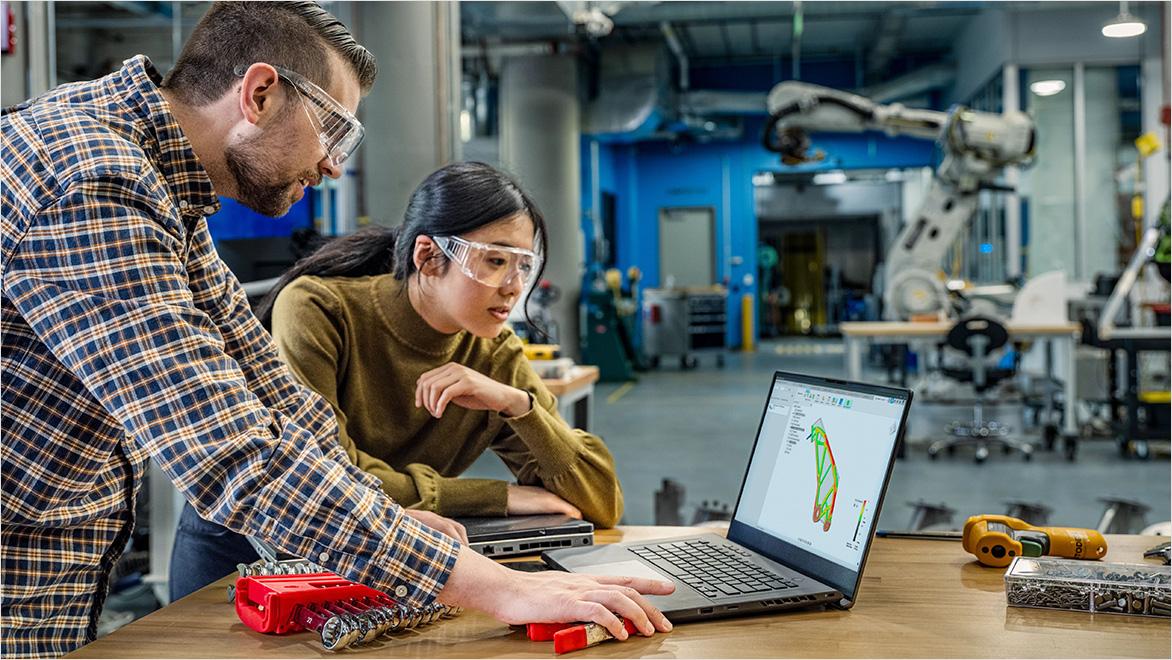
Autodesk’s suite of tools, including Fusion and AutoCAD, are at the forefront of enabling iterative design. These tools are user-friendly and packed with features that make it easy to create, test, and refine product designs.
Autodesk Fusion is useful for anyone working in 3D modelling and smart manufacturing. It offers an all-in-one platform where designers can sketch out their ideas, create 3D models, and run simulations to test how their designs will perform in the real world. The cloud-based software allows for easy collaboration and enables teams to work together no matter where they are.
But the real magic happens when we move from initial design to generative design—a process where Fusion suggests design options based on specific parameters and goals set by you. Generative design takes iterative design to the next level by offering a range of solution options you may never have considered.
Generative design is a revolutionary tool that leverages the power of AI and machine learning to explore all possible permutations of a solution. It is like having a team of designers working tirelessly to present you with the best options, each optimised for factors like weight, strength, cost, and material efficiency.
For industries like AEC, D&M, and M&E, generative design can lead to groundbreaking innovations. Imagine being able to create structures that are not only visually stunning but also optimised for materials and energy efficiency. Or consider manufacturing a component that’s lighter and stronger than anything that could be designed using traditional methods. These are the kinds of possibilities that generative design brings.
And the best part? Each generative design suggestion is just another iteration. You can tweak, refine, and iterate on these suggestions just as you would with a human-designed prototype. This synergy between human creativity and machine precision is where the future of design is headed.
The future is bright in India’s design and manufacturing industries, and iterative design plays an important role in shaping that future. To compete globally, speed to market and understanding users’ needs and preferences cannot be understated. Iterative design provides a structure for taking in feedback and rapidly prototyping solutions.
Autodesk’s software tools make it easier than ever to embrace iterative design and generative design. By using these tools, India’s manufacturers can stay ahead of the curve and continue to deliver innovative solutions that can serve customers and compete globally.
Analyze design options using AI-powered, generative design in Autodesk Fusion to create thousands of manufacturing-ready solutions.
Use the iterative design process to prototype quickly with Autodesk’s rapid prototyping software and create stunning 3D models for any aspects of your production cycle.
Get familiar with Autodesk Fusion and its powerful extensions that offer a suite of tools for iterative prototyping.
Iterative design is a process where designs are continuously improved through repeated cycles of prototyping, testing, and refining. It is crucial in modern manufacturing because it helps create better products by allowing for ongoing adjustments based on real-time feedback and testing.
Iterative design works hand-in-hand with 3D printing by enabling rapid prototyping. Manufacturers can quickly create, test, and adjust designs, leading to improved products in less time.
Benefits include speed and efficiency, cost savings, the ability to create more user-centric designs, and increased sustainability by reducing waste and emissions.
Smart manufacturing uses advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and robotics to optimise production. It complements iterative design by providing real-time data and automation, making it easier to refine designs and improve product quality.
Iterative design reduces costs by identifying and fixing issues early in the design process, avoiding expensive changes later. It also speeds up time-to-market by allowing faster prototyping and testing, which streamlines the development process.
Iterative design helps SMEs by allowing them to innovate faster and produce high-quality products without heavy upfront costs. This agility enables them to compete with larger companies on a global scale by offering customised, well-refined products.
Traditional design often follows a linear path with limited feedback loops, while iterative design is cyclical, with continuous prototyping and refinement. Iterative design is more flexible and adaptive, leading to better final products.